Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a common issue for individuals with diabetes and can lead to serious complications if not managed effectively. Controlling hyperglycemia at home is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing the long-term effects of uncontrolled diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, and neuropathy. This comprehensive guide will explore various strategies to manage hyperglycemia effectively at home, including dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, monitoring techniques, and when to seek medical help.
Understanding Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia occurs when blood glucose levels are higher than normal. This condition can arise due to several factors, including inadequate insulin production, insulin resistance, poor dietary choices, lack of physical activity, and stress. Managing hyperglycemia involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, in some cases, medication adjustments.
Why Controlling Hyperglycemia is Important
Consistently high blood glucose levels can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision problems. Effective management of hyperglycemia helps reduce the risk of these complications and improves overall quality of life.
Dietary Management
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for controlling hyperglycemia. This means consuming a variety of foods in the right proportions to maintain stable blood glucose levels. The key components of a balanced diet include:
Carbohydrates: Choose complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, legumes, and vegetables. These foods have a lower glycemic index and are digested more slowly, leading to more gradual increases in blood sugar.
Proteins: Incorporate lean protein sources like chicken, fish, tofu, and beans. Proteins help maintain muscle mass and can stabilize blood sugar levels.
Fats: Opt for healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil. These fats can improve insulin sensitivity and support overall health.
Portion Control
Managing portion sizes is crucial for controlling blood sugar levels. Eating large portions of even healthy foods can lead to spikes in blood glucose. Using smaller plates and bowls, and being mindful of portion sizes, can help manage calorie intake and blood sugar levels.
Meal Timing
Eating regular, well-balanced meals and snacks throughout the day can help prevent large fluctuations in blood glucose levels. Aim for three main meals and one or two snacks if needed. Avoid skipping meals, as this can lead to erratic blood sugar levels.
Glycemic Index (GI) Awareness
Understanding the glycemic index of foods can help in making better dietary choices. Foods with a low GI cause a slower, more gradual increase in blood sugar, while high-GI foods can cause rapid spikes. Focus on low-GI foods such as whole grains, non-starchy vegetables, and legumes.
Hydration
Adequate hydration is important for managing blood sugar levels. Drinking water throughout the day helps flush out excess glucose through urine and prevents dehydration, which can worsen hyperglycemia.
Physical Activity
Exercise and Blood Sugar Control
Regular physical activity is an effective way to manage hyperglycemia. Exercise helps improve insulin sensitivity, which allows your body to use glucose more efficiently. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming.
Strength Training
Incorporating strength training exercises, such as weight lifting or bodyweight exercises, at least two times per week can also benefit blood sugar control. Building muscle mass improves glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity.
Exercise Timing
Monitor your blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to understand how different activities affect your glucose levels. It’s essential to adjust your diet or insulin dosage as needed based on your activity levels.
Avoiding Sedentary Behavior
Prolonged periods of inactivity can contribute to hyperglycemia. Incorporate movement into your daily routine by taking short walks, standing up periodically, or using a standing desk if possible.
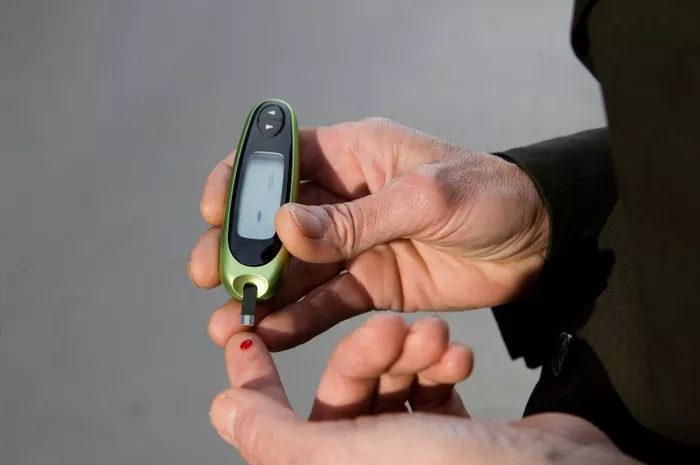
Monitoring Blood Glucose
Regular Testing
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for managing hyperglycemia. Use a blood glucose meter to check your levels as recommended by your healthcare provider. This helps you understand how different foods, activities, and medications affect your blood sugar.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Continuous glucose monitors provide real-time data on your blood glucose levels throughout the day. CGMs can offer valuable insights into blood sugar trends and help you make timely adjustments to your diet and medication.
Keeping a Blood Sugar Log
Maintaining a detailed log of your blood glucose readings, meals, physical activity, and medications can help identify patterns and triggers for high blood sugar. Share this log with your healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Medication Management
Understanding Medications
For some individuals, managing hyperglycemia may require medication. This can include oral medications that increase insulin sensitivity or insulin injections. It’s important to understand how each medication works and follow your healthcare provider’s instructions.
Medication Adherence
Consistently taking your prescribed medications as directed is crucial for controlling hyperglycemia. Set reminders or use a pill organizer to help you stay on track with your medication regimen.
Adjusting Medications
If you experience persistent hyperglycemia despite adhering to your medication regimen, consult your healthcare provider. They may need to adjust your medication or explore other treatment options.
Stress Management
The Impact of Stress on Blood Sugar
Stress can have a significant impact on blood glucose levels by increasing the production of stress hormones like cortisol. These hormones can lead to higher blood sugar levels and insulin resistance.
Stress-Reduction Techniques
Incorporate stress-reducing practices into your daily routine, such as:
Mindfulness and Meditation: Practices like mindfulness and meditation can help manage stress and improve emotional well-being.
Deep Breathing Exercises: Deep breathing exercises can help calm your mind and reduce stress.
Hobbies and Relaxation: Engage in activities you enjoy, such as reading, gardening, or listening to music, to help reduce stress levels.
Sleep and Blood Sugar
Importance of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep is vital for overall health and blood sugar management. Poor sleep can lead to insulin resistance and higher blood glucose levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night.
Sleep Hygiene Tips
Improve your sleep quality by:
Maintaining a Consistent Sleep Schedule: Go to bed and wake up at the same time each day.
Creating a Relaxing Bedtime Routine: Engage in calming activities before bed, such as reading or taking a warm bath.
Limiting Screen Time: Avoid screens at least an hour before bedtime to reduce exposure to blue light, which can interfere with sleep.
When to Seek Medical Help
Recognizing Warning Signs
While managing hyperglycemia at home is effective for many, there are times when you need to seek medical help. Be aware of the following warning signs:
Persistent Hyperglycemia: If your blood glucose levels remain high despite your efforts to control them, consult your healthcare provider.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemic Crisis: Symptoms such as severe nausea, vomiting, confusion, rapid breathing, and abdominal pain may indicate a hyperglycemic crisis, which requires immediate medical attention.
Uncontrolled Symptoms: If you experience symptoms of low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), such as dizziness, sweating, or shakiness, it’s essential to address them promptly and seek guidance from your healthcare provider.
Regular Medical Check-Ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for monitoring your overall health and diabetes management. They can provide personalized advice, adjust your treatment plan as needed, and address any concerns you may have.
See also: What Is Type 2 Diabetes with Hyperglycemia?
Conclusion
Controlling hyperglycemia at home requires a multifaceted approach that includes dietary management, physical activity, regular monitoring, medication adherence, stress management, and quality sleep. By implementing these strategies and working closely with your healthcare provider, you can effectively manage your blood glucose levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with uncontrolled diabetes.
Remember, effective diabetes management is a continuous process that involves making informed choices and staying vigilant about your health. Regularly review and adjust your management plan as needed to ensure optimal blood glucose control and overall well-being.
Related topics:
How to Manage Hyperglycemia Effectively