Controlled type 2 diabetes refers to effectively managing blood sugar levels within target ranges to prevent complications and maintain overall health. This article explores the definition of controlled diabetes type 2, strategies for achieving control, monitoring techniques, lifestyle considerations, and the importance of personalized care.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Definition and Pathophysiology
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. Insulin resistance occurs when cells fail to respond adequately to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Over time, the pancreas may produce less insulin, exacerbating the condition.
Impact on Health
Untreated or poorly controlled type 2 diabetes can lead to serious health complications, including cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, nerve damage (neuropathy), eye damage (retinopathy), and foot complications. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial to reducing these risks.
What is Controlled Type 2 Diabetes?
Defining Controlled Diabetes
Controlled type 2 diabetes means maintaining blood sugar levels within recommended target ranges set by healthcare providers. These targets aim to prevent hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), promoting overall health and reducing the risk of complications.
Blood Sugar Targets
The target blood sugar ranges for most adults with type 2 diabetes are generally:
- Fasting Blood Sugar (Before meals): 80-130 mg/dL (4.4-7.2 mmol/L)
- Postprandial Blood Sugar (1-2 hours after meals): Less than 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L)
Individual targets may vary based on factors such as age, duration of diabetes, presence of complications, and overall health status.
A1C Levels
The A1C test provides an average of blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. For most people with type 2 diabetes, the target A1C level is below 7%. This corresponds to an estimated average glucose (eAG) of around 154 mg/dL (8.6 mmol/L).
Strategies for Achieving and Maintaining Control
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy Eating
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake, portion sizes, and meal timing is crucial. Working with a registered dietitian can provide personalized guidance.
Regular Physical Activity
Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to use glucose more effectively. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with resistance training for muscle strength.
Medications and Insulin Therapy
Oral Medications
Many medications help lower blood sugar levels by improving insulin sensitivity, reducing glucose production in the liver, or enhancing insulin secretion. Examples include metformin, sulfonylureas, DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT-2 inhibitors.
Insulin Therapy
Some individuals with type 2 diabetes may require insulin therapy to achieve optimal blood sugar control. Insulin can be delivered via injections or insulin pumps, mimicking the body’s natural insulin production.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels at home helps individuals track their progress, make informed decisions about diet and exercise, and adjust medications as needed. SMBG involves using a blood glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels from a finger prick sample.
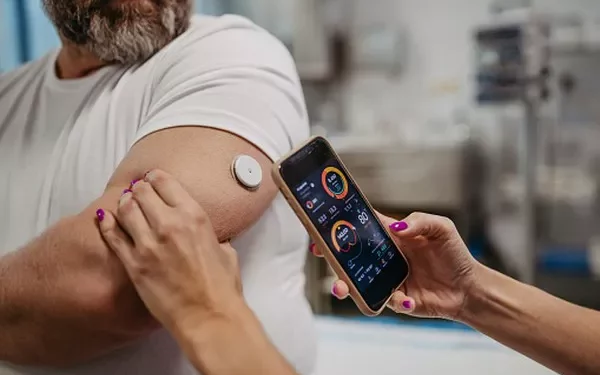
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM systems provide real-time data on blood sugar levels throughout the day and night. They consist of a sensor inserted under the skin that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. CGM devices can alert users to high or low blood sugar levels and trends.
Healthcare Team Collaboration
Diabetes Educators and Healthcare Providers
Working closely with a healthcare team, including physicians, diabetes educators, nurses, and dietitians, is essential for developing and adjusting a personalized diabetes management plan. Regular medical appointments allow for monitoring of progress, detection of complications, and adjustments to treatment as necessary.
Benefits of Controlled Type 2 Diabetes
Reduced Risk of Complications
Maintaining controlled blood sugar levels significantly reduces the risk of long-term complications associated with diabetes, such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems.
Improved Quality of Life
Effective management of type 2 diabetes enhances overall well-being by reducing symptoms, improving energy levels, and promoting better physical and mental health.
Long-Term Health and Independence
By controlling blood sugar levels and managing diabetes effectively, individuals can lead active, fulfilling lives while minimizing the impact of diabetes on daily activities and independence.
Challenges and Considerations
Individual Variability
Diabetes management is highly individualized, and achieving controlled blood sugar levels may require ongoing adjustments to lifestyle, medications, and treatment plans based on individual responses and changing circumstances.
Barriers to Control
Factors such as medication adherence, access to healthcare, socioeconomic status, mental health issues, and lifestyle habits can affect diabetes management and blood sugar control.
See also: What Is Metformin HCL Used to Treat?
Conclusion
In conclusion, controlled type 2 diabetes involves effectively managing blood sugar levels within target ranges to prevent complications and promote overall health. Through a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication therapy, regular blood sugar monitoring, and collaboration with healthcare providers, individuals with type 2 diabetes can achieve and maintain optimal blood sugar control. This proactive approach not only reduces the risk of long-term complications but also enhances quality of life and supports long-term health and well-being. Continuous education, support, and personalized care are essential components of successful diabetes management. Always consult with a healthcare provider for personalized guidance tailored to your specific needs and goals in managing type 2 diabetes effectively.
Related topics:
What Can I Do to Prevent Type 2 Diabetes?