Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of managing diabetes. Regular testing helps in maintaining blood sugar within the target range, avoiding complications, and understanding how different factors affect blood sugar levels. This article will delve into when and how often you should test your blood sugar, the best practices for testing, and how to interpret the results for optimal diabetes management.
Why Monitoring Blood Sugar is Important
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day based on various factors such as food intake, physical activity, stress, illness, and medications. Monitoring these levels provides valuable insights into how well your diabetes management plan is working and helps in making informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication.
Preventing Complications
Consistently high blood sugar levels can lead to complications such as heart disease, kidney disease, nerve damage, and vision problems. On the other hand, low blood sugar levels (hypoglycemia) can cause immediate symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and even loss of consciousness. Regular monitoring helps in preventing both high and low blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications.
When Should You Test Your Blood Sugar?
Factors Influencing Testing Frequency
The frequency of blood sugar testing varies based on the type of diabetes, the treatment plan, and individual health needs. Here are some general guidelines:
Type 1 Diabetes
For individuals with type 1 diabetes, frequent testing is essential. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends testing blood sugar levels multiple times a day, including:
- Before meals and snacks
- Before and after exercise
- Before bedtime
- Occasionally during the night
- When you are experiencing symptoms of high or low blood sugar
- During periods of stress or illness
Type 2 Diabetes
For individuals with type 2 diabetes, the frequency of testing can vary depending on the treatment plan:
For those on insulin therapy: Similar to type 1 diabetes, frequent testing is necessary. This includes testing before meals and at bedtime, and sometimes after meals or during the night.
For those on oral medications or lifestyle changes: The frequency of testing might be less but still important. Testing may include:
- Fasting blood sugar in the morning
- Before and after meals
- Occasionally at bedtime
Gestational Diabetes
For pregnant women with gestational diabetes, testing is typically done:
- Fasting blood sugar in the morning
- One to two hours after meals
- Before meals if taking insulin
Personalized Testing Schedule
Your healthcare provider will work with you to develop a personalized testing schedule based on your individual needs, treatment plan, and lifestyle. This schedule might change over time as your condition and treatment evolve.
Best Practices for Blood Sugar Testing
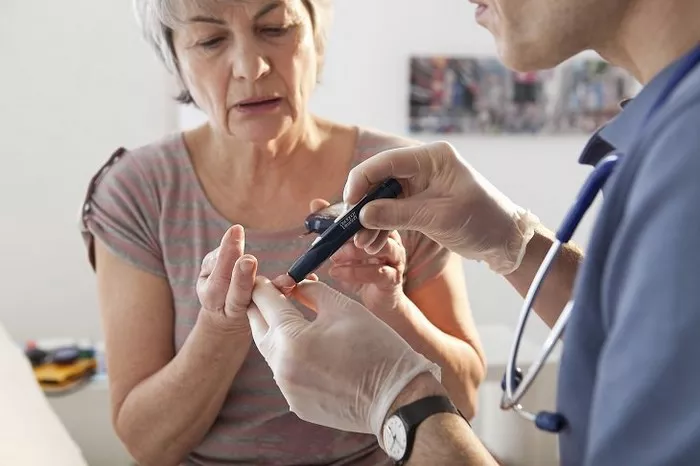
Using a Glucometer
A glucometer is a common device used for testing blood sugar levels. Here’s how to use it effectively:
- Wash your hands: Clean hands ensure accurate readings.
- Prepare the device: Insert a test strip into the glucometer.
- Prick your finger: Use a lancet to prick the side of your fingertip.
- Apply blood: Place a drop of blood on the test strip.
- Read the result: The glucometer will display your blood sugar level.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time blood sugar readings throughout the day and night. These devices consist of a sensor placed under the skin, a transmitter, and a receiver or smartphone app. CGMs can be particularly useful for individuals with type 1 diabetes or those experiencing frequent highs and lows.
Interpreting Blood Sugar Levels
Understanding what your blood sugar levels mean is crucial for effective management:
- Fasting blood sugar: This measures your blood sugar after not eating for at least 8 hours. A normal range is typically 70-99 mg/dL.
- Pre-meal blood sugar: Target range is generally 80-130 mg/dL.
- Post-meal blood sugar: This is measured 1-2 hours after eating. A target range is usually less than 180 mg/dL.
- Bedtime blood sugar: Ideal levels are typically between 100-140 mg/dL.
Your healthcare provider may provide different target ranges based on your individual needs.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
Diet
The type and amount of food you eat have a significant impact on your blood sugar levels. Carbohydrates, in particular, raise blood sugar levels more than proteins or fats. Monitoring your carbohydrate intake and understanding how different foods affect your blood sugar can help in maintaining control.
Physical Activity
Exercise generally lowers blood sugar levels, but the effect can vary depending on the type, intensity, and duration of activity. Regular physical activity is beneficial for overall diabetes management, but it’s important to monitor blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to avoid hypoglycemia.
Medications
Insulin and other diabetes medications play a crucial role in managing blood sugar levels. It’s important to take medications as prescribed and be aware of how they affect your blood sugar. Some medications may cause low blood sugar, so regular monitoring is essential.
Stress and Illness
Stress and illness can cause blood sugar levels to rise. During these times, you may need to test your blood sugar more frequently and adjust your treatment plan accordingly.
Strategies for Effective Blood Sugar Management
Keep a Blood Sugar Log
Maintaining a log of your blood sugar readings can help you and your healthcare provider identify patterns and make necessary adjustments to your treatment plan. Include the date, time, blood sugar level, food intake, physical activity, and any other factors that might affect your blood sugar.
Stay Consistent
Consistency is key in blood sugar management. Test your blood sugar at the same times each day, follow a regular eating schedule, and take your medications as prescribed.
Work with Your Healthcare Team
Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential for effective diabetes management. They can help you interpret your blood sugar readings, adjust your treatment plan, and provide support and guidance.
Education and Support
Educating yourself about diabetes and blood sugar management is crucial. Attend diabetes education classes, join support groups, and stay informed about new developments in diabetes care.
Advanced Blood Sugar Monitoring Techniques
Flash Glucose Monitoring
Flash glucose monitoring systems, such as the FreeStyle Libre, provide an alternative to traditional glucometers and CGMs. These devices allow you to check your blood sugar by scanning a sensor worn on the skin, providing readings without the need for finger pricks.
Smartphone Apps and Devices
Various smartphone apps and devices can help in tracking and managing blood sugar levels. These tools can sync with glucometers or CGMs, allowing you to log readings, track trends, and share data with your healthcare provider.
Remote Monitoring
Remote monitoring technologies enable healthcare providers to monitor your blood sugar levels in real-time, providing immediate feedback and support. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with unstable blood sugar levels or those who require close monitoring.
Challenges and Solutions in Blood Sugar Monitoring
Pain and Discomfort
Frequent finger pricks can be painful and uncomfortable. To minimize discomfort, use the sides of your fingertips, rotate testing sites, and use a lancet with adjustable depth settings. CGMs and flash glucose monitors can also reduce the need for finger pricks.
Cost and Accessibility
The cost of testing supplies, glucometers, CGMs, and other devices can be a barrier for some individuals. Check with your insurance provider to understand your coverage, and explore programs and resources that offer financial assistance for diabetes supplies.
Maintaining Motivation
Staying motivated to test your blood sugar regularly can be challenging. Set realistic goals, celebrate small achievements, and seek support from your healthcare provider, family, and friends.
See also: What’s Dangerous Blood Sugar Level
Conclusion
Regular blood sugar testing is a cornerstone of effective diabetes management. By understanding when and how often to test, using the right tools, and interpreting the results correctly, you can maintain control over your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications. Work closely with your healthcare team, stay informed, and make adjustments as needed to ensure optimal diabetes management.
Related topics:
What Are The Types Of Blood Sugar Tests