Blood glucose monitors, also known as glucometers, are essential tools for individuals with diabetes. These devices play a critical role in monitoring blood sugar levels, helping to manage diabetes effectively, and preventing complications. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of blood glucose monitors, their functionality, types, and their significance in diabetes care.
Introduction to Blood Glucose Monitoring
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar. Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for people with diabetes to avoid short-term and long-term complications, such as cardiovascular disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and vision problems.
Blood glucose monitors are devices designed to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood. They provide real-time data that helps individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication. By regularly monitoring their blood glucose levels, individuals can maintain them within a target range and reduce the risk of complications.
How Blood Glucose Monitors Work
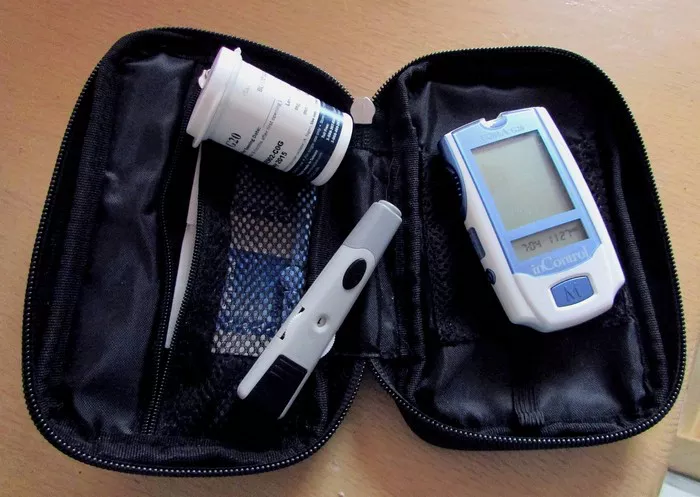
Blood glucose monitors are relatively simple to use, consisting of a few basic components:
Test Strips: These are disposable strips that contain chemicals that react with glucose in the blood.
Lancing Device: A small, spring-loaded device that holds a lancet (a tiny needle) used to prick the skin to obtain a blood sample.
Meter: The electronic component that reads the test strip and displays the blood glucose level.
The Testing Process
The process of measuring blood glucose typically involves the following steps:
Preparing the Meter: Ensure that the meter is clean and properly calibrated. Insert a new test strip into the meter.
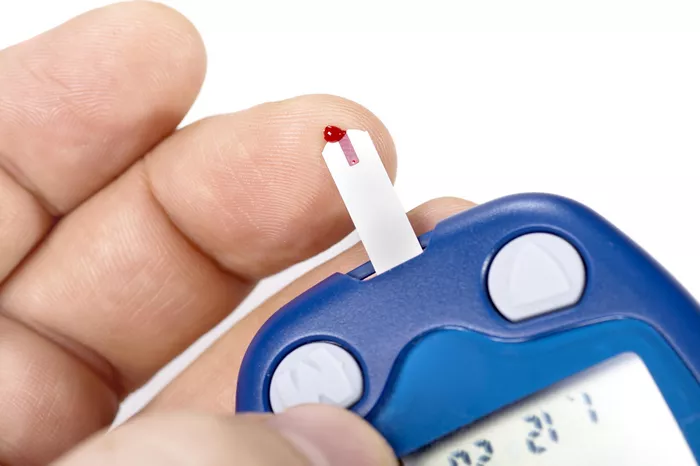
Obtaining a Blood Sample: Use the lancing device to prick the side of the fingertip (or an alternate site, if recommended). Squeeze gently to produce a small drop of blood.
Applying the Blood: Touch the drop of blood to the edge of the test strip. The strip will draw the blood into a tiny chamber where the chemical reaction occurs.
Reading the Result: Within a few seconds, the meter will display the blood glucose level on its screen.
The chemical reaction on the test strip involves glucose oxidase, an enzyme that reacts with glucose to produce an electrical signal. The meter measures this signal and converts it into a blood glucose level, usually expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
Types of Blood Glucose Monitors
There are several types of blood glucose monitors available, each with its unique features and benefits. The choice of monitor depends on various factors, including the individual’s lifestyle, budget, and specific medical needs.
Basic Blood Glucose Monitors
These are the most common type of glucometers and are typically affordable and easy to use. They provide accurate readings and are suitable for most individuals with diabetes. Basic monitors require manual coding of test strips and usually store a limited number of previous readings.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Continuous glucose monitors are more advanced devices that provide real-time blood glucose readings throughout the day and night. They consist of a sensor placed under the skin that measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. The sensor sends data to a receiver or a smartphone app, providing continuous monitoring.
CGMs offer several advantages over traditional glucometers:
- Continuous Data: CGMs provide a comprehensive view of glucose trends, helping users understand how their levels fluctuate throughout the day.
- Alerts and Alarms: CGMs can alert users to high or low blood sugar levels, allowing for prompt action.
- Data Analysis: These devices often come with software that analyzes glucose patterns, providing valuable insights for managing diabetes.
Flash Glucose Monitors
Flash glucose monitors are similar to CGMs but do not provide continuous real-time data. Instead, users must scan a sensor with a reader or smartphone to obtain a glucose reading. These monitors are less expensive than CGMs and still offer the convenience of frequent monitoring without fingersticks.
Smart Glucose Monitors
Smart glucose monitors are connected devices that sync with smartphones or other digital devices. They often come with apps that track and analyze glucose data, helping users manage their diabetes more effectively. These monitors can provide reminders for testing, insulin dosing advice, and trend analysis.
Importance of Blood Glucose Monitoring
Regular blood glucose monitoring is crucial for managing diabetes and preventing complications. Here are some key reasons why monitoring is important:
Personalized Diabetes Management
Each individual’s response to food, physical activity, stress, and medication can vary significantly. Regular monitoring helps individuals understand how these factors affect their blood glucose levels, enabling personalized diabetes management. This tailored approach can help maintain blood glucose levels within the target range and reduce the risk of complications.
Preventing Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) are common issues for individuals with diabetes. Regular monitoring helps detect these conditions early, allowing for prompt treatment. Untreated hypoglycemia can lead to confusion, seizures, and loss of consciousness, while prolonged hyperglycemia can cause damage to organs and tissues.
Adjusting Medications
Medications, including insulin, play a crucial role in managing diabetes. Blood glucose monitoring helps healthcare providers and individuals with diabetes adjust medication dosages based on current glucose levels. This ensures that medications are working effectively and reduces the risk of side effects.
Assessing the Impact of Lifestyle Changes
Diet, physical activity, and stress management are important components of diabetes care. Monitoring blood glucose levels helps individuals assess the impact of lifestyle changes on their glucose levels. For example, they can determine how different foods affect their blood sugar and adjust their diet accordingly.
Detecting Trends and Patterns
Regular monitoring allows individuals to detect trends and patterns in their blood glucose levels. For example, they may notice that their glucose levels tend to spike after certain meals or drop during specific times of the day. Identifying these patterns can help in making informed decisions about diet, activity, and medication.
Challenges and Limitations of Blood Glucose Monitoring
While blood glucose monitors are indispensable tools, there are some challenges and limitations associated with their use:
Accuracy and Reliability
The accuracy of blood glucose monitors can be influenced by several factors, including user technique, test strip quality, and environmental conditions. Inaccurate readings can lead to improper diabetes management. Continuous advancements in technology aim to improve the accuracy and reliability of these devices.
Cost
The cost of blood glucose monitoring can be a barrier for some individuals. Basic glucometers and test strips can be relatively affordable, but advanced devices like CGMs and flash glucose monitors can be expensive. Additionally, the ongoing cost of test strips and sensors can add up over time.
User Compliance
Consistent monitoring requires diligence and discipline, which can be challenging for some individuals. Factors such as discomfort from finger pricks, inconvenience, and forgetfulness can lead to inconsistent monitoring. Education and support from healthcare providers can help improve compliance.
Data Overload
For individuals using CGMs or smart glucose monitors, the sheer volume of data can be overwhelming. Interpreting this data correctly and making appropriate decisions can be complex. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in helping individuals understand and use this data effectively.
Innovations in Blood Glucose Monitoring
The field of blood glucose monitoring is continuously evolving, with ongoing research and technological advancements aimed at improving the accuracy, convenience, and affordability of these devices.
Non-Invasive Monitors
One area of active research is the development of non-invasive blood glucose monitors. These devices aim to measure glucose levels without the need for finger pricks or sensors inserted under the skin. Technologies being explored include infrared spectroscopy, optical sensors, and saliva-based testing.
Integrated Systems
Another promising innovation is the integration of blood glucose monitors with other diabetes management tools, such as insulin pumps and smart devices. These integrated systems can automate insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings, providing a more seamless and effective diabetes management solution.
Enhanced Data Analytics
Advancements in data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) are also enhancing blood glucose monitoring. AI algorithms can analyze large amounts of glucose data to identify patterns, predict future glucose levels, and provide personalized recommendations. This can help individuals make more informed decisions and improve their diabetes management.
Wearable Technology
Wearable technology, such as smartwatches and fitness trackers, is being integrated with blood glucose monitoring systems. These devices can provide continuous glucose monitoring and real-time alerts, making it easier for individuals to stay on top of their glucose levels throughout the day.
Conclusion
Blood glucose monitors are indispensable tools for individuals with diabetes, providing critical information for effective diabetes management. From basic glucometers to advanced continuous glucose monitors, these devices have revolutionized the way diabetes is managed, offering real-time data, alerts, and comprehensive insights into blood glucose patterns.
Despite the challenges and limitations, the benefits of regular blood glucose monitoring are undeniable. It empowers individuals to take control of their diabetes, make informed decisions, and reduce the risk of complications. Ongoing innovations in this field promise to make blood glucose monitoring even more accurate, convenient, and accessible, further enhancing the quality of life for individuals with diabetes.
As we look to the future, the integration of advanced technologies, non-invasive monitoring, and AI-driven analytics will continue to transform diabetes care. By staying informed about these developments and utilizing the latest tools and techniques, individuals with diabetes can achieve better outcomes and live healthier, more fulfilling lives.