Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels resulting from either insufficient insulin production or ineffective utilization of insulin by the body. There are several types of diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, gestational diabetes, and other less common forms. Regardless of the type, diabetes can have significant implications for overall health and quality of life.
Role of Blood Sugar Monitoring
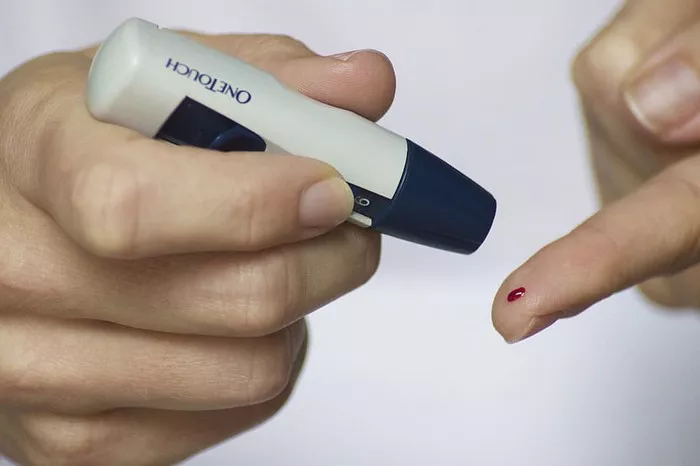
Blood sugar monitoring plays a crucial role in managing diabetes and preventing complications. By regularly monitoring blood sugar levels, individuals with diabetes can track their progress, identify patterns, and make informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication. Monitoring allows for early detection of high or low blood sugar levels, enabling prompt intervention to prevent complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hypoglycemia.
Medical Care for Diabetes
Comprehensive medical care for diabetes patients includes regular check-ups with healthcare providers, medication management, and lifestyle counseling. Healthcare providers play a crucial role in monitoring overall health, assessing blood sugar control, adjusting medications as needed, and providing guidance on healthy lifestyle habits. Medications for diabetes may include insulin, oral medications, or other injectable therapies to help regulate blood sugar levels.
Preventing Complications
Monitoring blood sugar levels and receiving appropriate medical care can help prevent or delay diabetes-related complications such as heart disease, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. By maintaining optimal blood sugar control and managing other risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol levels, individuals with diabetes can reduce their risk of developing serious complications and improve their overall health outcomes.
Blood Sugar Levels and Targets
Recommended blood sugar targets may vary depending on individual factors such as age, health status, and diabetes type. However, general targets for blood sugar levels include:
Fasting blood sugar: Typically, fasting blood sugar levels should be between 80 to 130 mg/dL (4.4 to 7.2 mmol/L) for individuals with diabetes.
Postprandial blood sugar: Target ranges for postprandial blood sugar levels (1 to 2 hours after meals) may be between 80 to 180 mg/dL (4.4 to 10 mmol/L) for individuals with diabetes.
Achieving and maintaining these targets requires diligent monitoring, medication adherence, and lifestyle modifications.
Monitoring Technology
Advances in blood sugar monitoring technology have revolutionized diabetes management, providing individuals with more convenient and accurate ways to track their blood sugar levels. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are wearable devices that continuously measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, providing real-time data and trends. CGMs offer advantages such as reducing the need for finger pricks, providing alerts for high or low blood sugar levels, and facilitating better decision-making regarding diet, exercise, and medication.
Interpreting Data
Interpreting monitoring data involves analyzing blood sugar readings and identifying trends and patterns over time. By understanding how various factors such as diet, exercise, stress, and medication affect blood sugar levels, individuals can make informed decisions to optimize their diabetes management. Healthcare providers can also assist in interpreting monitoring data and developing personalized care plans tailored to individual needs and goals.
Collaboration with Healthcare Providers
Collaboration with healthcare providers is essential for effective diabetes management. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals can receive personalized guidance, support, and education to help them achieve their blood sugar targets and reduce their risk of complications. Healthcare providers can also assist in coordinating care with other specialists, such as dietitians, diabetes educators, and mental health professionals, to address the various aspects of diabetes management.
Lifestyle Impact
Lifestyle choices, including diet and physical activity, have a significant impact on blood sugar levels and overall diabetes management. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods, with an emphasis on fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats, can help regulate blood sugar levels and promote overall health. Regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, swimming, or cycling, can improve insulin sensitivity, reduce blood sugar levels, and lower the risk of complications associated with diabetes.
Resources and Support
For further education and support, individuals with diabetes can access a variety of resources, including:
American Diabetes Association (ADA): Offers educational materials, online resources, support groups, and advocacy efforts to raise awareness about diabetes and support individuals affected by the condition.
Diabetes support groups: Joining a diabetes support group, either in person or online, can provide a sense of community, encouragement, and practical tips for managing blood sugar levels and coping with the challenges of living with diabetes.
Healthcare providers: Healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, endocrinologists, and diabetes educators, can provide personalized guidance, support, and education to help individuals manage their diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding diabetes and the importance of blood sugar monitoring is essential for effective diabetes management and prevention of complications. By monitoring blood sugar levels regularly, receiving appropriate medical care, and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals with diabetes can achieve better blood sugar control, reduce their risk of complications, and improve their overall quality of life. With the support of healthcare providers, resources, and peer support networks, individuals with diabetes can navigate their diabetes journey with confidence and achieve better health outcomes.
Related Topics:
What Do High Blood Sugar Levels Mean?