Hypoglycemia and diabetes are two distinct yet interconnected conditions that affect blood sugar levels in the body. Understanding the differences between them is crucial for managing and preventing complications associated with both. In this article, we will explore the definitions, causes, risk factors, and potential links between hypoglycemia and diabetes, as well as the importance of monitoring, prevention, and seeking medical advice.
Definition of Hypoglycemia and Diabetes
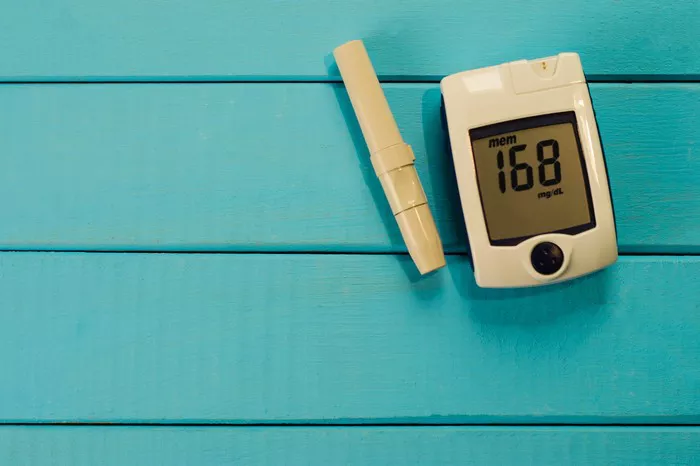
Hypoglycemia is a medical condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels, typically below 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). It can occur when the body’s glucose levels drop too low, leading to symptoms such as sweating, shakiness, confusion, and weakness. On the other hand, diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. Common symptoms of diabetes include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision.
Causes of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can be caused by various factors, including:
Excessive insulin or medication: Taking too much insulin or certain diabetes medications can lower blood sugar levels beyond the normal range.
Inadequate food intake: Skipping meals or not consuming enough carbohydrates can result in hypoglycemia.
Excessive physical activity: Engaging in intense or prolonged exercise without adjusting insulin doses or carbohydrate intake can deplete glucose stores.
Alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol, especially on an empty stomach, can interfere with liver function and glucose production.
Hormonal imbalances: Disorders such as adrenal insufficiency or growth hormone deficiency can affect glucose metabolism.
Certain medical conditions: Liver disorders, critical illness, or insulinoma (a pancreatic tumor) can also lead to hypoglycemia.
Risk Factors for Diabetes
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing diabetes, including:
Genetics: Family history of diabetes can increase the risk of developing the condition.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for type 2 diabetes.
Sedentary lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Poor diet: Consuming a diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of diabetes.
Age: The risk of diabetes increases with age, particularly after the age of 45.
Ethnicity: Certain ethnic groups, such as African Americans, Hispanic Americans, and Native Americans, are at higher risk of developing diabetes.
Potential Link Between Hypoglycemia and Diabetes
While hypoglycemia itself does not cause diabetes, recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia may indicate underlying insulin resistance or impaired glucose metabolism, which are common features of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes. Insulin resistance occurs when cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels over time.
Importance of Monitoring and Prevention
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and recognizing the signs of both hypoglycemia and diabetes are essential for managing these conditions effectively. Lifestyle modifications, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing weight, and attending regular medical check-ups, can help prevent the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
Consultation with Healthcare Provider
Individuals who are concerned about their risk of diabetes or experiencing recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia should consult with a healthcare provider for proper evaluation, diagnosis, and management. Healthcare professionals can provide personalized advice and guidance tailored to individual needs and circumstances, helping to optimize blood sugar control and overall health.
conclusion
Understanding the relationships between hypoglycemia and diabetes is essential for effectively managing these conditions and preventing complications. By recognizing the signs, addressing risk factors, and seeking medical advice when needed, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of developing diabetes or experiencing hypoglycemic episodes.
Related Topics:
How To Do When You Get Hypoglycemia?