Hypoglycemia, characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels, is a critical concern for individuals with diabetes and others. Managing and preventing hypoglycemia involves understanding its triggers and implementing effective strategies. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of hypoglycemia triggers and management strategies to empower individuals to maintain optimal blood sugar control and overall health.
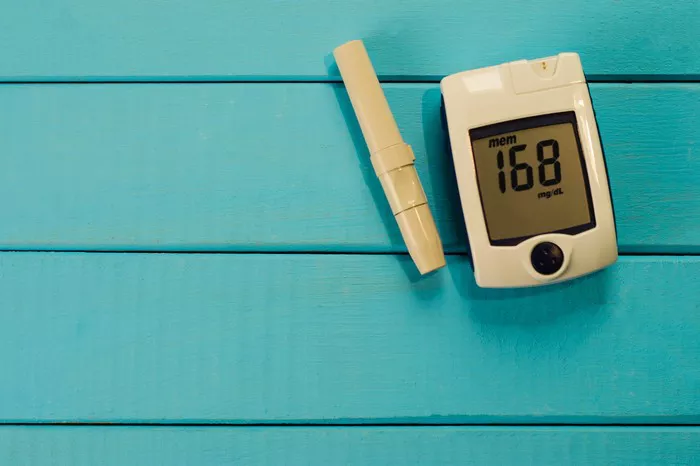
Hypoglycemia is a medical condition characterized by abnormally low blood sugar levels, typically below 70 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). It can lead to symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe complications if left untreated.
Understanding Hypoglycemia Triggers
Various factors or situations can trigger hypoglycemia, including:
Skipping or delaying meals: Not eating on time or missing meals disrupts the body’s glucose supply, leading to drops in blood sugar levels.
Excessive insulin or diabetes medication: Taking too much insulin or certain diabetes medications lowers blood sugar levels beyond the normal range.
Inadequate carbohydrate intake: Consuming meals low in carbohydrates or not enough to balance medication doses can result in hypoglycemia.
Strenuous physical activity: Engaging in intense or prolonged exercise without adjusting insulin doses or carbohydrate intake depletes glucose stores and causes hypoglycemia.
Alcohol consumption: Drinking alcohol, especially on an empty stomach, interferes with liver function and glucose production, leading to hypoglycemia.
Hormonal imbalances: Disorders like adrenal insufficiency or pituitary disorders affect glucose metabolism and trigger hypoglycemia.
Illness or infections: During illness, the body’s energy demands increase, necessitating adjustments in medication doses or dietary intake to prevent hypoglycemia.
Changes in medication or treatment regimen: Starting new medications or making changes to existing diabetes treatment plans can affect blood sugar levels and increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Individual Factors:It’s essential to highlight that hypoglycemia triggers vary among individuals based on factors such as age, medical history, medication regimen, and lifestyle habits. What triggers hypoglycemia in one person may not affect another in the same way.
Management Strategies
To effectively manage and prevent hypoglycemia, consider the following strategies:
Following a regular meal schedule with balanced carbohydrate intake: Eating consistent meals and snacks containing carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats helps stabilize blood sugar levels.
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly: Regular monitoring, especially before and after meals, physical activity, or other factors that may affect blood sugar, helps individuals adjust their management plan accordingly.
Communicating with healthcare providers: Keep healthcare providers informed about any changes in medication, treatment plans, or symptoms experienced to ensure appropriate adjustments and management.
Being prepared with fast-acting carbohydrates: Carry fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, fruit juice, or candy, to promptly treat hypoglycemic episodes.
Implementing lifestyle changes: Make lifestyle adjustments like moderating alcohol consumption, adjusting physical activity levels, and managing stress to minimize the risk of hypoglycemia.
Conclusion
Understanding hypoglycemia triggers and implementing proactive management and prevention strategies are crucial for maintaining optimal blood sugar control and overall health. Encourage individuals to work closely with their healthcare team to identify and address individual triggers for hypoglycemia, ultimately empowering them to lead healthier lives.
Related Topics:
What Glucose Level Is Hypoglycemia?