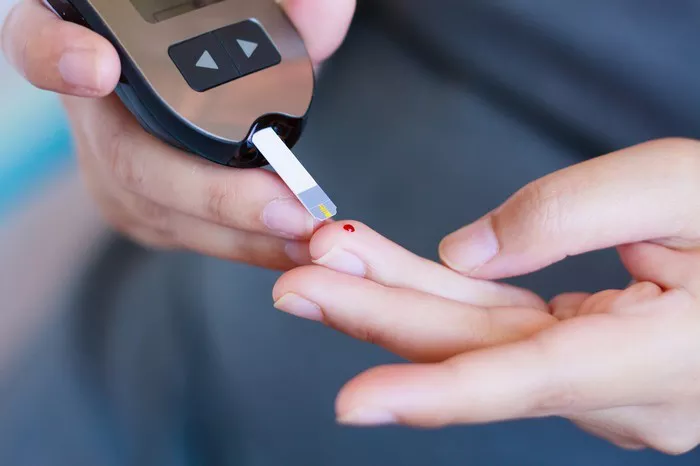
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels, which can have profound effects on overall health and well-being. In this article, we will explore the importance of blood sugar (glucose) levels, normal ranges, factors influencing variations, targets for diabetes management, health impacts, monitoring and management strategies, and lifestyle factors affecting blood sugar levels.
what are blood sugar levels?
Blood sugar levels refer to the concentration of glucose present in the bloodstream. Glucose serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, fueling essential physiological processes such as muscle contraction, brain function, and cellular metabolism. Maintaining optimal blood sugar levels is crucial for supporting overall health, energy metabolism, and proper functioning of various organs and systems within the body.
Normal Blood Sugar Range:
For fasting blood sugar levels, the typical normal range falls between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). After meals, blood sugar levels may temporarily rise, but they should return to normal within a few hours. Postprandial (after-meal) blood sugar targets may vary slightly, but generally aim to remain below 180 mg/dL to minimize the risk of hyperglycemia.
Variations in Blood Sugar Levels:
Blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day due to various factors such as meals, physical activity, stress, and medication. Carbohydrate-rich meals, for example, can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels, while physical activity can enhance insulin sensitivity and promote glucose uptake by cells. Stress and illness may lead to temporary spikes in blood sugar, highlighting the intricate interplay between physiological and psychological factors.
Blood Sugar Targets for Diabetes Management:
For individuals with diabetes, maintaining blood sugar levels within target ranges is essential for preventing complications and optimizing health outcomes. Fasting blood sugar targets typically range from 80 to 130 mg/dL, while postprandial targets may be set below 180 mg/dL. Long-term glycemic control goals, as measured by hemoglobin A1c levels, should ideally be less than 7% to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Impact of Blood Sugar Levels on Health
Maintaining blood sugar levels within the recommended range is critical for overall health and well-being. Both low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) and high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) levels can have significant health risks. Hypoglycemia can cause symptoms such as dizziness, confusion, and loss of consciousness, while hyperglycemia can lead to long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, and vision problems.
Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels:
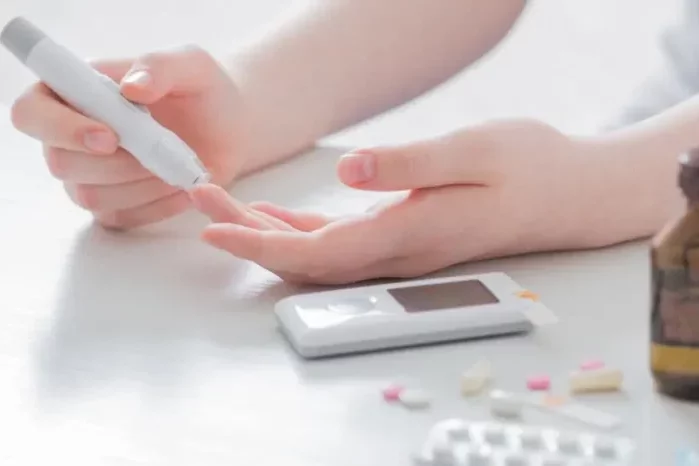
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes to assess their condition and make informed decisions about treatment and lifestyle adjustments. This may involve self-monitoring using a blood glucose meter or continuous glucose monitoring system. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of fluctuations and timely intervention to prevent complications.
Managing Blood Sugar Levels:
Effective management strategies for blood sugar levels include dietary modifications, regular physical activity, medication adherence, stress management techniques, and regular medical check-ups. Carbohydrate counting, glycemic index awareness, and portion control can help individuals with diabetes make informed food choices and maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day.
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Blood Sugar:
Several lifestyle factors can affect blood sugar levels, including diet, exercise, sleep patterns, alcohol consumption, smoking, and stress. Making healthy lifestyle choices such as consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, getting adequate sleep, limiting alcohol intake, quitting smoking, and practicing stress management techniques can help promote stable blood sugar levels and overall well-being.
Conclusion
Managing blood sugar levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes and anyone striving for optimal health. By understanding the importance of blood sugar levels, monitoring regularly, adhering to targets for diabetes management, and making healthy lifestyle choices, individuals can effectively manage their condition and reduce the risk of complications. Empowering individuals with knowledge and support enables them to take control of their health and lead fulfilling lives despite the challenges of diabetes.
Related Topics:
Do Any Smart Watches Measure Blood Sugar?