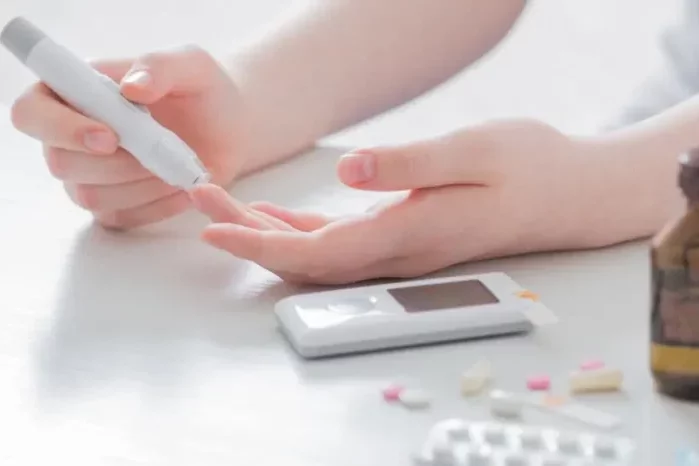
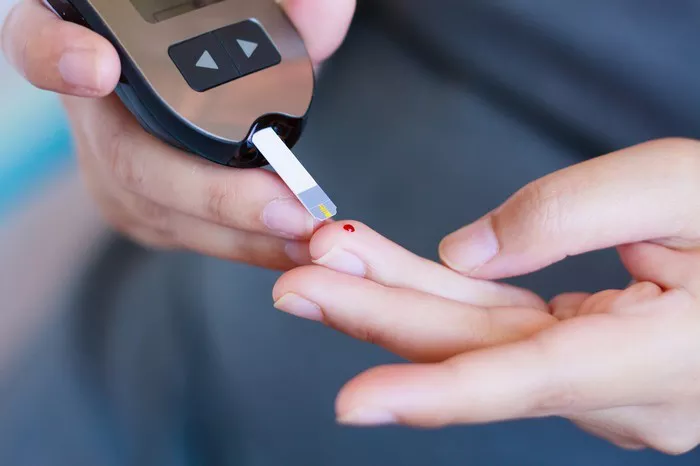
Blood glucose levels, also known as blood sugar levels, refer to the concentration of glucose present in the bloodstream. Glucose serves as the primary source of energy for the body’s cells, fueling various physiological processes and supporting overall health and functioning.
Normal Blood Glucose Levels:
For individuals without diabetes, the recommended target range for fasting blood glucose levels is typically between 70 and 100 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL). Pre-meal (before eating) blood glucose levels should ideally fall within this range as well. After eating, blood glucose levels may rise temporarily, with post-meal levels typically peaking around 120 mg/dL or below two hours after a meal.
Several factors can influence blood glucose levels, including diet and nutrition, physical activity levels, stress and emotions, and medications and medical conditions. Carbohydrates, in particular, have a significant impact on blood glucose levels, as they are broken down into glucose during digestion. Physical activity can help lower blood glucose levels by increasing glucose uptake into the muscles for energy.
Factors Affecting Blood Glucose Levels
Interpreting blood glucose test results involves understanding the context in which the tests were conducted and considering factors such as recent meals and physical activity levels. It’s essential to recognize that blood glucose levels can vary throughout the day and may be influenced by various factors. Monitoring trends over time can provide valuable insights into an individual’s blood glucose control and help identify patterns or trends that may require adjustment.
Blood glucose levels are influenced by a variety of factors, both controllable and uncontrollable. Understanding these factors is essential for individuals with diabetes to effectively manage their condition and for anyone interested in optimizing their overall health.
1. Diet and Nutrition:
Diet plays a significant role in determining blood glucose levels. Carbohydrates, found in foods such as bread, pasta, fruits, and sweets, have the most significant impact on blood glucose levels because they are broken down into glucose during digestion. However, other macronutrients, including protein and fat, can also affect blood glucose levels, albeit to a lesser extent.
2. Physical Activity Levels:
Physical activity has a significant impact on blood glucose levels. Exercise increases the body’s sensitivity to insulin, allowing cells to more effectively absorb glucose from the bloodstream for energy. As a result, regular physical activity can help lower blood glucose levels and improve overall glucose control.
3. Stress and Emotions:
Stress and emotions can affect blood glucose levels through the release of stress hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can cause blood glucose levels to rise as part of the body’s “fight or flight” response. Additionally, stress and negative emotions may lead to changes in eating habits and physical activity levels, further impacting blood glucose control.
4. Medications and Medical Conditions:
Certain medications and medical conditions can influence blood glucose levels. For example, some medications, such as corticosteroids, can cause blood glucose levels to rise, while others, such as insulin or oral diabetes medications, are used to lower blood glucose levels. Additionally, medical conditions such as hormonal imbalances, infections, or illnesses can affect blood glucose control.
Prevention and Management Strategies
Maintaining normal blood glucose levels is essential for overall health and well-being. Strategies for preventing and managing abnormal blood glucose levels include following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins; engaging in regular physical activity; monitoring blood glucose levels as recommended by healthcare providers; taking medications as prescribed for individuals with diabetes; and seeking medical advice for managing abnormal blood glucose levels.
Consulting with a healthcare provider is crucial for personalized guidance on blood glucose management. Healthcare providers can offer individualized recommendations based on an individual’s medical history, lifestyle, and treatment goals. It’s essential for individuals to discuss any concerns or questions about their blood glucose levels with their healthcare team.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding blood glucose levels and effectively managing them is essential for individuals living with diabetes or at risk of developing the condition. By following recommended guidelines for monitoring blood glucose levels, making lifestyle changes, and seeking medical advice as needed, individuals can take control of their blood glucose management and reduce their risk of complications associated with abnormal blood glucose levels. Empowered with knowledge and support from healthcare providers, individuals can lead healthy and fulfilling lives despite the challenges of diabetes.
Related Topics: