In today’s digital age, wearable technology has revolutionized the way we monitor our health and wellness. Among these innovations, smartwatches have gained popularity for their multi-functional capabilities, offering features such as heart rate monitoring, activity tracking, and sleep analysis. However, one area that has garnered significant attention is their potential for blood sugar monitoring, especially for individuals living with diabetes. In this article, we delve into the intersection of diabetes management and wearable technology, exploring the current landscape, limitations, technological challenges, and future possibilities of using smartwatches for blood sugar monitoring.
Smartwatches and Their Common Functionalities
Smartwatches are wearable devices that combine the functionalities of traditional watches with advanced computing capabilities. They typically feature touchscreen interfaces, wireless connectivity, and a variety of sensors for monitoring health metrics and tracking daily activities. Common functionalities include:
Heart rate monitoring: Smartwatches use optical sensors to measure heart rate continuously throughout the day, providing insights into cardiovascular health.
Activity tracking: Built-in accelerometers and gyroscopes track movement and calculate metrics such as steps taken, distance traveled, and calories burned.
Sleep analysis: Some smartwatches offer sleep tracking features, monitoring sleep patterns and providing insights into sleep quality.
Blood Sugar Monitoring and Its Significance
Blood sugar monitoring, also known as blood glucose monitoring, is crucial for individuals with diabetes to manage their condition effectively. It involves measuring the concentration of glucose in the blood, which helps individuals make informed decisions about medication, diet, and lifestyle choices. Regular monitoring allows for early detection of fluctuations in blood sugar levels, reducing the risk of complications associated with diabetes, such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
Current Limitations of Smartwatches in Measuring Blood Sugar Levels
While smartwatches offer a range of health monitoring features, such as heart rate monitoring, activity tracking, and sleep analysis, their ability to measure blood sugar levels directly is limited. As of now, there are no mainstream smartwatches that offer built-in blood sugar monitoring capabilities. However, some smartwatch manufacturers have started exploring this area, with rumors of upcoming models featuring glucose monitoring sensors.
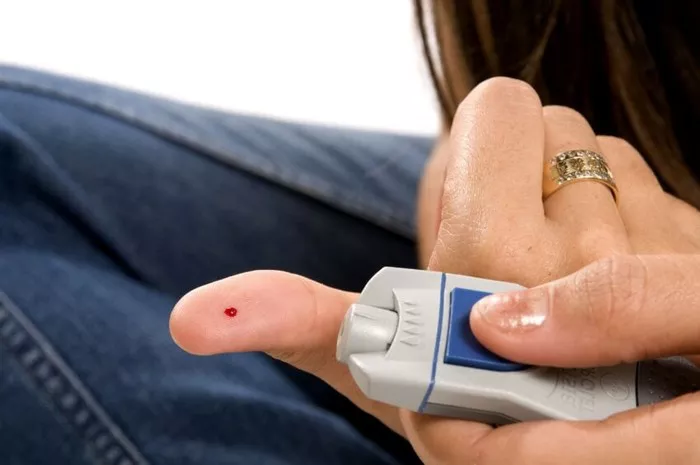
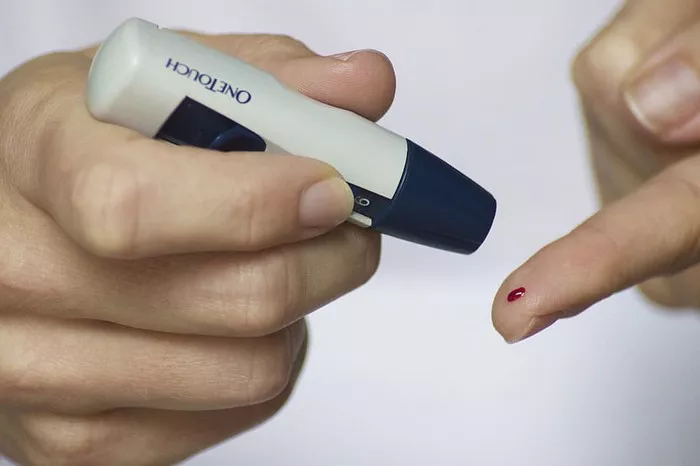
The primary limitation of smartwatches in measuring blood sugar levels is the lack of reliable and accurate sensors for glucose monitoring. Unlike other health metrics such as heart rate or activity level, glucose levels cannot be measured noninvasively through the skin. Current methods for measuring blood glucose levels require a blood sample, typically obtained through finger-prick testing using a glucometer.
Developing a reliable blood sugar monitoring feature for smartwatches presents several technological challenges. One of the main challenges is achieving accurate glucose measurements without the need for invasive blood sampling. Optical sensors and other non-invasive techniques are being explored, but they must overcome issues such as sensor accuracy, interference from ambient light, and variations in skin characteristics.
Calibration requirements pose another challenge, as glucose monitoring sensors need to be calibrated regularly to maintain accuracy. Furthermore, regulatory considerations, such as obtaining approval from health authorities for medical-grade devices, add complexity to the development and commercialization process.
Advancements and Future Possibilities
Despite the current limitations, there are promising advancements and ongoing research in the field of wearable technology and blood sugar monitoring. Researchers are exploring innovative approaches, such as using sweat or interstitial fluid to measure glucose levels non-invasively. Advances in sensor technology, data processing algorithms, and machine learning techniques hold the potential to improve the accuracy and reliability of glucose monitoring in smartwatches.
In the absence of built-in blood sugar monitoring features in smartwatches, individuals with diabetes have alternative solutions for monitoring their glucose levels. Dedicated glucose monitoring devices, such as glucometers and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) systems, offer more accurate and reliable measurements. Glucometers require a blood sample for testing, while CGM systems use sensors implanted under the skin to continuously monitor glucose levels throughout the day.
For individuals who prioritize blood sugar monitoring and are considering purchasing a smartwatch, it is essential to set realistic expectations. While smartwatches offer valuable health monitoring features, they currently lack the ability to measure blood glucose levels directly. When evaluating different smartwatch models, consider factors such as battery life, compatibility with smartphone apps for diabetes management, and overall usability for health tracking purposes.
Conclusion
While smartwatches hold promise as wearable devices for health monitoring, their current capabilities for blood sugar monitoring are limited. Despite ongoing advancements and research in the field, challenges such as sensor accuracy, calibration requirements, and regulatory considerations must be addressed before smartwatches can provide reliable glucose monitoring capabilities. In the meantime, individuals with diabetes can rely on alternative solutions such as dedicated glucose monitoring devices and continuous glucose monitoring systems for accurate blood sugar monitoring. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about advancements in wearable technology and consulting reliable sources for updates will be essential for individuals managing diabetes and seeking innovative solutions for health monitoring.
Related Topics:
Do You Know How To Lower Blood Sugar Immediately?
What Can I Eat Immediately To Lower My Blood Sugar?
What Should You Eat Immediately If Your Blood Sugar Is High?