Receiving a diagnosis of type 1 diabetes (T1D) can be a life-altering moment, requiring individuals to adapt to a new reality of managing their health and well-being. While the initial shock and uncertainty may feel overwhelming, it’s essential to approach the situation with knowledge, resilience, and a proactive mindset. In this comprehensive guide, we explore the steps individuals can take after being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes to effectively manage their condition, optimize their health, and live life to the fullest.
Understanding Type 1 Diabetes: What You Need to Know
Type 1 diabetes is a chronic autoimmune disorder characterized by the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to absolute insulin deficiency. Without insulin, the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar levels, resulting in hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and a range of symptoms, including increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and weight loss.
Unlike type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity and sedentary behavior, type 1 diabetes is not preventable and is not caused by diet or lifestyle choices. Instead, T1D is believed to result from a combination of genetic susceptibility and environmental triggers, such as viral infections or exposure to certain toxins, that provoke an immune-mediated attack on pancreatic beta cells.
Key Steps to Take After Being Diagnosed with Type 1 Diabetes
- Education and Information: Educate yourself about type 1 diabetes, including its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and potential complications. Knowledge is power, and understanding your condition will empower you to make informed decisions about your health and well-being.
- Build a Support Network: Surround yourself with a supportive network of family members, friends, healthcare providers, and fellow individuals with diabetes who can offer guidance, encouragement, and empathy. Connecting with others who understand what you’re going through can provide invaluable emotional support and practical advice.
- Develop a Diabetes Management Plan: Work with your healthcare team to develop a personalized diabetes management plan that addresses your unique needs, goals, and preferences. This plan may include strategies for blood sugar monitoring, insulin therapy, carbohydrate counting, physical activity, and stress management.
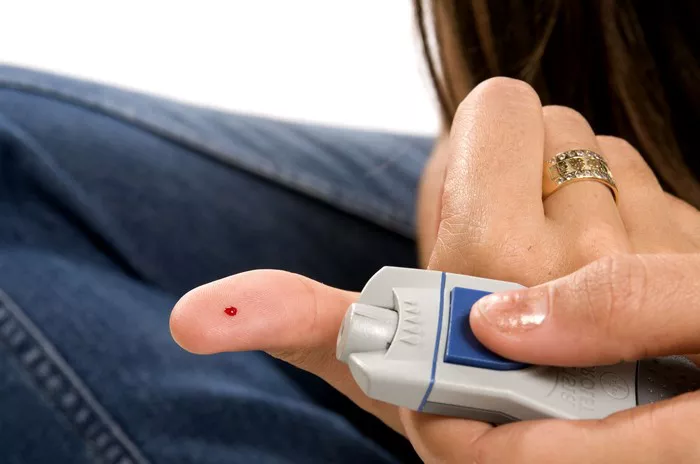
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly monitor your blood sugar levels using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system to track changes and trends in your blood sugar levels. This information will help you make informed decisions about insulin dosing, dietary choices, and lifestyle adjustments.
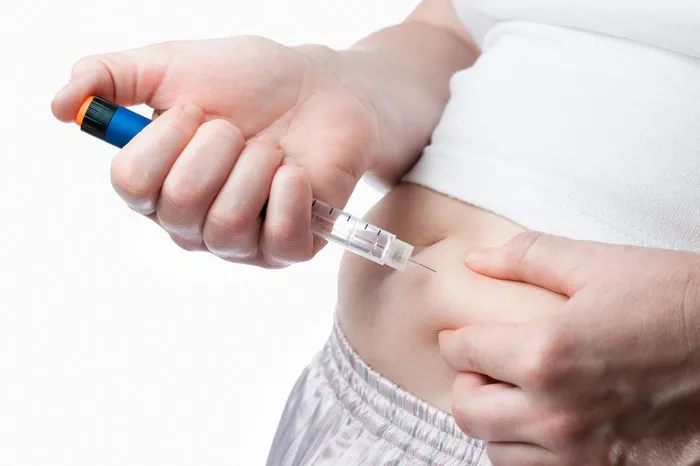
- Insulin Therapy: Follow your prescribed insulin regimen as directed by your healthcare provider. Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for type 1 diabetes and is necessary to replace the insulin that your body cannot produce. Work closely with your healthcare team to adjust your insulin doses as needed based on your blood sugar levels, dietary intake, physical activity, and other factors.
- Healthy Eating: Adopt a balanced and nutritious diet that supports stable blood sugar levels and overall health. Focus on whole, minimally processed foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Monitor your carbohydrate intake, and space your meals and snacks evenly throughout the day to prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes.
- Physical Activity: Incorporate regular physical activity into your daily routine to improve insulin sensitivity, control blood sugar levels, and promote cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing.
- Stress Management: Find healthy ways to manage stress and prioritize self-care to maintain emotional well-being and support blood sugar control. Techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, yoga, journaling, and spending time in nature can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
- Regular Healthcare Visits: Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to monitor your diabetes management, assess your overall health, and address any concerns or questions you may have. These appointments provide an opportunity to review your blood sugar levels, adjust your treatment plan, and screen for potential complications.
- Stay Informed: Stay up-to-date on the latest developments in diabetes research, treatment options, and self-management strategies. Knowledge is constantly evolving, and staying informed will empower you to take control of your diabetes and advocate for your health.
Challenges and Coping Strategies for Living with Type 1 Diabetes
Living with type 1 diabetes presents unique challenges and obstacles that may require adaptation and resilience. Some common challenges faced by individuals with T1D include:
- Fear of Hypoglycemia: Fear of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) can lead to anxiety and reluctance to take insulin or engage in physical activity. It’s essential to recognize the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia and have a plan in place to treat it promptly with fast-acting carbohydrates.
- Managing Blood Sugar Variability: Blood sugar levels can fluctuate unpredictably due to factors such as stress, illness, hormonal changes, and medication interactions. Learning to recognize patterns and trends in your blood sugar levels and adjusting your treatment plan accordingly can help minimize variability and optimize control.
- Diabetes Burnout: Diabetes management can be demanding and overwhelming at times, leading to feelings of burnout, frustration, or resentment. It’s important to acknowledge these feelings and seek support from your healthcare team, loved ones, or mental health professionals as needed.
- Social and Emotional Impact: Living with a chronic condition like diabetes can have a significant social and emotional impact, affecting relationships, self-esteem, and quality of life. Finding ways to connect with others, express your feelings, and prioritize self-care can help foster resilience and emotional well-being.
Conclusion: Empowering Life with Type 1 Diabetes
Being diagnosed with type 1 diabetes can feel like a daunting and life-changing experience, but it’s important to remember that with knowledge, support, and proactive management, individuals with T1D can lead full, active, and fulfilling lives. By taking steps to educate yourself about your condition, develop a personalized diabetes management plan, and cultivate a supportive network of healthcare providers and loved ones, you can navigate the challenges of diabetes with confidence and resilience.
Remember that you are not alone in your journey with type 1 diabetes. Reach out for support, seek guidance from your healthcare team, and embrace self-compassion as you navigate the ups and downs of managing your diabetes. With dedication, perseverance, and a positive attitude, you can thrive with type 1 diabetes and achieve your health goals, one day at a time.