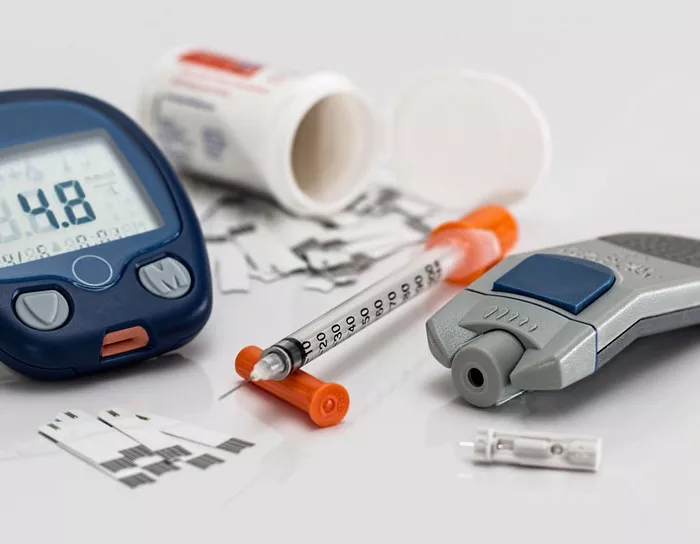
Autoimmune diabetes, including type 1 diabetes, is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s immune system mistakenly attacking insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. This autoimmune attack leads to a deficiency in insulin production, resulting in high blood sugar levels and the need for lifelong management. While there is currently no cure for autoimmune diabetes, several treatment approaches aim to control blood sugar levels, prevent complications, and improve overall quality of life for individuals living with the condition.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the various treatment options available for autoimmune diabetes, including medications, insulin therapy, lifestyle modifications, and emerging therapies.
Understanding Autoimmune Diabetes
Before delving into treatment options, it’s essential to understand the underlying mechanisms of autoimmune diabetes. In autoimmune diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly identifies beta cells in the pancreas as foreign invaders and launches an attack against them. This autoimmune attack leads to the destruction of beta cells, impairing the pancreas’s ability to produce insulin—a hormone necessary for regulating blood sugar levels. As a result, individuals with autoimmune diabetes require external insulin replacement therapy to manage their condition effectively.
Medications for Autoimmune Diabetes
1. Insulin Therapy:
Insulin therapy is the cornerstone of treatment for individuals with autoimmune diabetes. It involves injecting insulin subcutaneously to replace the insulin that the pancreas can no longer produce. Various types of insulin are available, including rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, and long-acting formulations, each designed to mimic the body’s natural insulin secretion patterns.
2. Glucose-Lowering Medications:
In addition to insulin therapy, some individuals with autoimmune diabetes may benefit from oral or injectable medications that help lower blood sugar levels. These medications include:
3. Metformin:
A commonly prescribed oral medication that improves insulin sensitivity and reduces glucose production in the liver.
4. GLP-1 receptor agonists:
Injectable medications that stimulate insulin secretion and suppress glucagon secretion, leading to lower blood sugar levels and potential weight loss.
5. SGLT2 inhibitors:
Oral medications that work by blocking the reabsorption of glucose by the kidneys, resulting in increased urinary glucose excretion and lower blood sugar levels.
Lifestyle Modifications
1. Healthy Eating Habits:
Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help individuals with autoimmune diabetes manage their blood sugar levels and maintain overall health. Monitoring carbohydrate intake, portion sizes, and meal timing can also play a crucial role in blood sugar management.
2. Regular Physical Activity:
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as aerobic exercise, strength training, or yoga, can help improve insulin sensitivity, lower blood sugar levels, and promote cardiovascular health. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, or as recommended by a healthcare provider.
Emerging Therapies and Research
1. Beta Cell Replacement Therapies:
Researchers are exploring innovative approaches to replace or regenerate beta cells in individuals with autoimmune diabetes. These therapies include pancreatic islet transplantation, stem cell therapy, and gene therapy, which hold the potential to restore insulin production and improve blood sugar control.
2. Immunomodulatory Therapies:
Immunomodulatory therapies aim to modulate the immune system’s response to prevent or slow down the autoimmune destruction of beta cells. These therapies may include immunosuppressive drugs, monoclonal antibodies, or other immune-modulating agents, which are currently undergoing clinical trials.
Conclusion
In conclusion, treatment for autoimmune diabetes involves a multifaceted approach aimed at controlling blood sugar levels, preventing complications, and enhancing quality of life. From insulin therapy and glucose-lowering medications to lifestyle modifications and emerging therapies, individuals with autoimmune diabetes have a range of options available to help them manage their condition effectively.
By working closely with healthcare providers, staying informed about the latest advancements in diabetes management, and adopting healthy lifestyle habits, individuals with autoimmune diabetes can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their condition.