Managing prediabetes is an essential part of preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes. One of the most crucial aspects of managing prediabetes is monitoring blood sugar levels. For many people, checking blood sugar at home is a natural progression in their care regimen. But should prediabetic individuals be checking their blood sugar at home? In this article, we will explore the advantages and limitations of home blood sugar monitoring for prediabetes, the proper techniques, and how these measurements can inform decisions for better health management.
Understanding Prediabetes and Its Risks
Before diving into whether home blood sugar monitoring is necessary, it’s important to understand what prediabetes is and why it’s such a significant health condition. Prediabetes occurs when blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. It’s often a silent condition with few symptoms, but it puts individuals at a much higher risk of developing full-blown diabetes, as well as cardiovascular diseases and stroke.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that nearly 1 in 3 adults in the United States has prediabetes, though most are unaware of it. Early detection and intervention, including lifestyle changes such as weight management, healthy eating, and regular exercise, are critical for reversing the condition and preventing the development of diabetes.
For individuals diagnosed with prediabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels is an effective tool to track how well their management strategies are working. The question is whether home blood sugar monitoring is appropriate for everyone with prediabetes or if it’s just for those who have already developed diabetes.
The Importance of Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is vital for individuals with diabetes, but it can also be important for people with prediabetes. Here’s why:
1. Early Detection of Changes
Home blood sugar monitoring allows individuals with prediabetes to detect any fluctuations in their blood sugar levels over time. If blood sugar levels begin to rise, it can serve as an early warning sign, alerting individuals and their healthcare providers that intervention may be needed to prevent progression to type 2 diabetes.
2. Tracking the Impact of Lifestyle Changes
Lifestyle changes, such as adjusting diet and exercise habits, play a pivotal role in managing prediabetes. Monitoring blood sugar levels at home allows individuals to see the immediate effects of their actions. For example, tracking blood sugar before and after meals can help individuals understand how different foods affect their glucose levels. This knowledge can guide future meal planning and make it easier to identify foods that may need to be limited or avoided.
3. Empowerment and Accountability
When individuals can track their own health, they often feel more empowered and responsible for their well-being. For those with prediabetes, seeing positive changes in blood sugar levels can be a motivational boost to continue healthy habits. Conversely, seeing a rise in blood sugar levels can act as a prompt to modify their behavior and seek guidance from a healthcare provider.
4. Avoiding Complications
Prediabetes itself is not usually associated with symptoms. However, when blood sugar levels consistently remain high, even in the prediabetic range, it can lead to long-term complications. These include damage to the heart, kidneys, and nerves. Regular blood sugar monitoring ensures that any concerning changes can be addressed before they lead to complications.
Should People with Prediabetes Monitor Their Blood Sugar at Home?
While the advantages of home blood sugar monitoring are clear, it’s essential to examine whether it’s necessary for everyone with prediabetes.
Benefits of Home Monitoring for Prediabetes
For some individuals, especially those with risk factors for diabetes, home monitoring can be incredibly beneficial. Here are a few reasons why checking blood sugar at home might be a good idea:
Peace of Mind and Proactive Management : Some people feel more at ease knowing they can check their blood sugar levels at home. Having control over monitoring can be particularly comforting for those who are more aware of the risks of type 2 diabetes and wish to take a proactive role in managing their health.
Tracking Progress : Prediabetes management often involves lifestyle modifications that take time to show results. Home monitoring provides a way to track progress, giving individuals feedback on whether their strategies are effective. If blood sugar levels drop over time, this can reinforce their efforts, providing validation for their actions.
A Personalized Approach : Home monitoring allows individuals to personalize their approach. By testing at different times of day and before or after meals, they can develop a clearer picture of how various activities and foods impact their blood sugar levels. This personalization may be more useful than relying solely on clinical visits, where blood sugar readings represent a snapshot rather than a comprehensive view.
Informed Conversations with Healthcare Providers : Regular monitoring can provide valuable data for discussions with healthcare providers. Sharing these readings during medical visits can help clinicians better understand an individual’s health trajectory and make more informed decisions about their care plan.
Limitations of Home Blood Sugar Monitoring for Prediabetes
However, not everyone with prediabetes needs to check their blood sugar at home. Here are some reasons why home monitoring might not be necessary for some individuals:
No Symptoms : Many individuals with prediabetes have no symptoms, which can make home monitoring feel unnecessary or even anxiety-inducing. In the absence of symptoms, some individuals may not feel the need for regular blood sugar checks unless advised by their doctor.
Cost and Accessibility :Regular blood sugar monitoring requires purchasing a glucose meter and test strips, which can be costly. For some, especially those without insurance or those with limited access to healthcare resources, the cost of home monitoring may be prohibitive. Additionally, not everyone is comfortable with or skilled at using the necessary equipment, which could lead to inaccurate readings and unnecessary stress.
No Clear Actionable Data : While monitoring blood sugar is useful, simply knowing the numbers may not always lead to actionable decisions, especially for those with mild prediabetes. In many cases, lifestyle changes—such as eating a balanced diet and increasing physical activity—are enough to manage blood sugar levels. Monitoring alone won’t improve health outcomes without significant lifestyle adjustments, and some individuals may feel overwhelmed or confused by the numbers without expert interpretation.
Dependence on Regular Medical Check-ups :For many individuals with prediabetes, a few visits to a healthcare provider per year may be sufficient for monitoring blood sugar levels. Healthcare providers can conduct tests like the hemoglobin A1c, which provides a long-term picture of blood sugar control, and offer guidance on lifestyle changes. For these individuals, regular medical appointments might be more efficient and cost-effective than home monitoring.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar at Home
If you or a loved one with prediabetes decides to monitor blood sugar at home, it’s crucial to do so correctly to ensure accuracy and reliability. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Choosing a Blood Glucose Meter
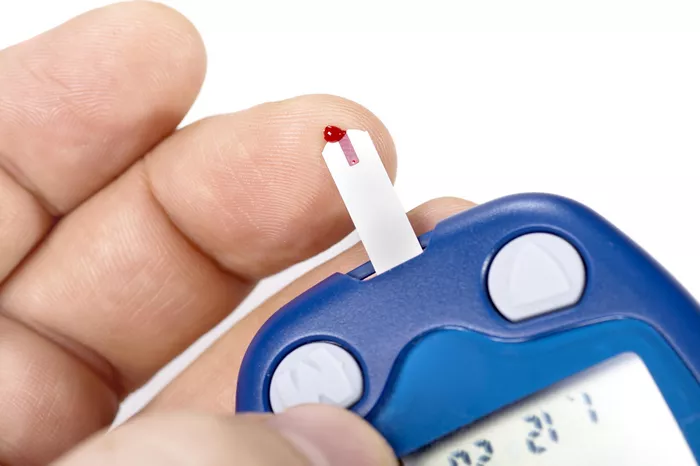
There are many types of blood glucose meters available, so it’s important to choose one that suits your needs. Look for one that is easy to use, provides accurate results, and offers features like memory storage to track your readings. Most devices require a small blood sample obtained by pricking your fingertip, but some newer models allow for alternate site testing, such as the forearm or thigh.
2. Testing Your Blood Sugar
To test your blood sugar, you will need a lancing device (a small needle used to prick the skin), test strips, and a glucose meter. Wash your hands before using the device, as dirt or food residues can affect the accuracy of the results. Place a small drop of blood onto the test strip, and the meter will display your blood sugar level. It’s essential to follow the instructions provided with your meter to ensure proper technique.
3. When to Test
For people with prediabetes, testing can be done at different times of the day. Testing before meals and 1-2 hours after meals can help understand how food affects your blood sugar. If you’re tracking the impact of exercise or medication, it’s helpful to test before and after these activities to monitor any changes in glucose levels.
4. Understanding Your Results
Blood sugar levels can fluctuate throughout the day. Generally, prediabetic individuals may see fasting blood sugar levels between 100 and 125 mg/dL. After meals, blood sugar levels should typically remain below 180 mg/dL. However, individual targets may vary, so it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare provider about your specific goals and action steps based on your readings.
Conclusion: Is Home Blood Sugar Monitoring Right for You?
The decision to monitor blood sugar at home as a person with prediabetes depends on a variety of factors, including personal preference, healthcare guidance, and the overall approach to managing the condition. While home monitoring can provide valuable insights into how lifestyle changes are affecting blood sugar levels, it is not always necessary for everyone. Regular consultations with a healthcare provider and making appropriate lifestyle modifications are also effective ways to prevent the progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes.
For those who choose to monitor their blood sugar at home, proper technique, a clear understanding of what the readings mean, and open communication with healthcare providers are essential components of effective management. Ultimately, the goal of blood sugar monitoring—whether at home or through regular check-ups—is to help prevent the onset of type 2 diabetes and promote a healthier, more active life.
By using blood sugar monitoring effectively and as part of a comprehensive approach, individuals with prediabetes can take charge of their health, make informed decisions, and prevent the development of more serious health conditions in the future.
Related topics: