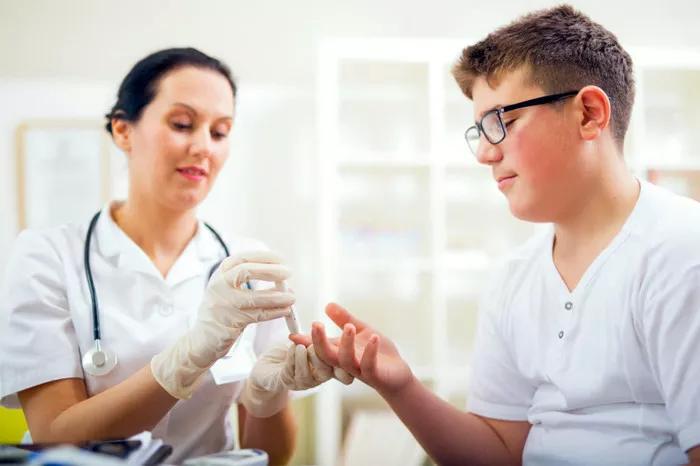
A One Touch glucose meter is a crucial device for individuals with diabetes to monitor their blood sugar levels accurately and conveniently. It provides a quick and relatively easy way to obtain essential information about one’s blood glucose concentration. This enables patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding diet, exercise, and medication adjustments. Understanding how this device operates is not only beneficial for those using it but also for healthcare professionals involved in diabetes management and education.
The Basic Components
The Meter Itself
The One Touch glucose meter is a compact and portable electronic device. It has a display screen that shows the measured blood glucose level. The meter is designed to be user-friendly, with simple buttons for navigation and operation. For example, it usually has a power button to turn it on and off and a button to start the testing process. The body of the meter is often made of durable plastic, ensuring it can withstand regular use and handling. It also has a port or slot where the test strip is inserted. This connection is crucial as it allows the meter to communicate with the test strip and obtain the necessary data for glucose measurement.
Test Strips
Test strips are an essential part of the One Touch glucose meter system. These thin, rectangular strips are made of a special material that can react with the glucose in a blood sample. Each strip has a small area at one end that comes into contact with the blood. This area contains chemicals that undergo a specific reaction when glucose is present. For instance, the glucose in the blood may cause an enzyme on the strip to catalyze a reaction that generates an electrical signal. The test strips are usually single-use and need to be stored properly to maintain their accuracy. They are often packaged in a sealed container to protect them from moisture and other environmental factors that could affect their performance.
The Testing Process
Pricking the Finger
Before using the One Touch glucose meter, the user needs to obtain a small blood sample. This is typically done by pricking the fingertip with a lancet. The lancet is a small, sharp needle that is designed to cause minimal pain. It is inserted into a lancet device, which allows the user to control the depth of the prick. For example, some lancet devices have adjustable settings, so the user can choose a depth that is comfortable for them. Once the finger is pricked, a small drop of blood will form. It is important to ensure that the blood droplet is of an appropriate size. If it is too small, the test strip may not be able to obtain an accurate reading.
Applying the Blood Sample
After obtaining the blood droplet, the user quickly applies it to the end of the test strip. The test strip has a capillary action that draws the blood into the reaction area. This process must be done carefully and within a specific time frame. For example, most One Touch test strips require the blood to be applied within a few seconds after pricking the finger. Once the blood enters the reaction area of the test strip, the chemical reaction begins. The glucose in the blood reacts with the enzymes and other substances on the strip, leading to a series of changes that will ultimately result in a measurable signal.
Data Storage and Management
Memory Capacity
One Touch glucose meters usually have a built-in memory to store blood glucose readings. The memory capacity can vary from model to model. Some meters can store hundreds of readings, which is beneficial for tracking blood sugar levels over time. For example, a patient can review their past week’s or month’s readings to look for patterns. This can help them and their healthcare provider identify trends, such as whether their blood sugar is consistently high or low at certain times of the day. The stored data can also be used to assess the effectiveness of a treatment plan, such as a new diet or medication regimen.
Connectivity and Data Transfer
Many modern One Touch glucose meters have connectivity features. They can connect to a computer or a smartphone via Bluetooth or a USB cable. This allows for easy data transfer. For example, a patient can sync their meter with a diabetes management app on their smartphone. The app can then analyze the data, create graphs and charts, and even send reminders for testing or medication. Some meters can also connect to a cloud service, enabling healthcare providers to access the patient’s blood sugar data remotely. This improves communication between the patient and the provider and allows for more timely and accurate management of diabetes.
Tips for Using and Maintaining
Proper Usage
To get accurate and reliable results from a One Touch glucose meter, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully. This includes using the correct type of test strip for the meter, ensuring the lancet is clean and sharp, and properly cleaning the finger before pricking. For example, washing the hands with soap and warm water and drying them thoroughly can help reduce the risk of contamination. Also, make sure to apply the blood sample to the test strip within the recommended time frame and in the correct amount.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance of the One Touch glucose meter is essential. Keep the meter clean by wiping it with a soft, dry cloth. Store it in a cool, dry place, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. If the meter is not working properly, check the batteries first. Low batteries can cause inaccurate readings or other malfunctions. If the problem persists, refer to the user manual for troubleshooting steps. For example, if the meter is displaying an error code, the manual can provide information on what the code means and how to fix the issue. It is also a good idea to have a backup meter in case the primary one fails.
Conclusion
The One Touch glucose meter is a valuable tool in diabetes management. By understanding its components, testing process, measurement principle, accuracy factors, data storage and management features, and proper usage and maintenance, users can ensure that they obtain accurate and useful blood glucose readings. This, in turn, helps in better controlling blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Related topics