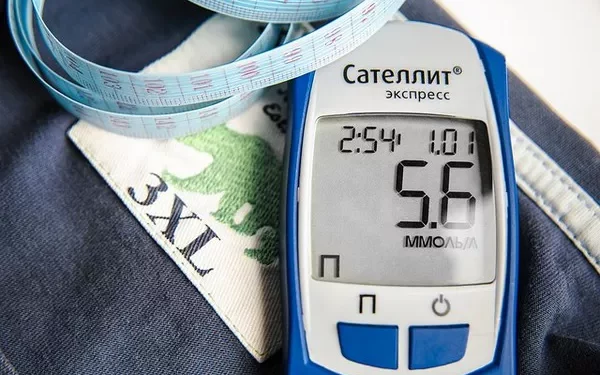
Monitoring blood sugar levels is a crucial aspect of diabetes management. Understanding what constitutes a normal average daily blood sugar level is essential for maintaining health and preventing complications associated with diabetes. This article will provide a comprehensive overview of normal blood sugar levels, how they are measured, factors affecting blood sugar, and tips for maintaining healthy levels.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
What Is Blood Sugar?
Blood sugar, or blood glucose, refers to the amount of glucose present in the blood. Glucose is the primary source of energy for the body’s cells. It is obtained from the food we eat, particularly carbohydrates, and is regulated by hormones, primarily insulin. Insulin helps glucose enter the cells, reducing blood sugar levels.
Why Is Monitoring Blood Sugar Important?
Monitoring blood sugar is vital for several reasons:
Preventing Complications: Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications, including heart disease, nerve damage, kidney failure, and eye problems.
Managing Diabetes: For individuals with diabetes, regular monitoring helps in adjusting medication, diet, and physical activity levels.
Identifying Patterns: Tracking blood sugar levels can help identify trends and patterns, aiding in better diabetes management.
Normal Blood Sugar Levels
What Is Considered Normal?
Normal blood sugar levels can vary based on several factors, including the time of measurement (fasting or after meals) and the individual’s overall health. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) provides the following guidelines for normal blood sugar levels:
Fasting Blood Sugar: 70 to 99 mg/dL (milligrams per deciliter) when tested after an overnight fast.
Postprandial Blood Sugar: Less than 140 mg/dL two hours after eating.
A1C Levels: An average blood glucose level of less than 5.7% over the past three months.
What Is Average Daily Blood Sugar?
Average daily blood sugar is calculated using various blood glucose readings taken throughout the day. The American Diabetes Association recommends keeping an average blood sugar level within the following ranges:
For individuals without diabetes: 70 to 140 mg/dL.
For individuals with diabetes: Ideally, the average should be under 180 mg/dL after meals and under 130 mg/dL before meals.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within these ranges is critical for overall health and preventing complications associated with diabetes.
How to Measure Blood Sugar Levels
1. Blood Glucose Meters
Blood glucose meters are handheld devices that measure blood sugar levels. The process involves the following steps:
Pricking the Finger: A small drop of blood is obtained by pricking the fingertip with a lancet.
Applying Blood to Test Strip: The blood is placed on a test strip inserted into the meter.
Reading the Result: The meter displays the blood sugar level within seconds.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Continuous glucose monitors provide real-time blood sugar readings. They consist of a small sensor inserted under the skin, which measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. CGMs offer several advantages:
Real-Time Monitoring: Users receive continuous updates on their blood sugar levels.
Alerts for High or Low Levels: Many CGMs can alert users when their blood sugar is too high or too low.
Trend Data: CGMs provide insights into how blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day.
3. Laboratory Tests
For a comprehensive assessment, healthcare providers may order laboratory tests:
Fasting Blood Sugar Test: A blood sample is taken after fasting for at least eight hours.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT): This test involves fasting overnight, consuming a glucose solution, and measuring blood sugar levels at intervals.
Hemoglobin A1C Test: This test provides an average blood sugar level over the past two to three months by measuring the percentage of glucose attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Factors Affecting Blood Sugar Levels
1. Diet
What we eat plays a significant role in blood sugar levels. Key dietary factors include:
Carbohydrate Intake: Foods high in carbohydrates, such as bread, pasta, and sugary snacks, can cause blood sugar levels to rise. It is essential to manage carbohydrate intake by choosing complex carbohydrates, which are digested more slowly.
Fiber Content: High-fiber foods can help stabilize blood sugar levels by slowing down digestion and preventing spikes. Foods rich in fiber include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
Meal Timing: Eating regular meals and snacks can help maintain stable blood sugar levels. Skipping meals can lead to fluctuations.
2. Physical Activity
Exercise is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity helps:
Lower Blood Sugar Levels: Exercise increases insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to use glucose more effectively.
Promote Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the risk of developing insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
3. Stress
Stress can significantly impact blood sugar levels. When the body is under stress, it releases hormones like cortisol and adrenaline, which can raise blood sugar levels. Managing stress through techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, and physical activity can help stabilize blood sugar.
4. Hormonal Changes
Hormones can influence blood sugar levels. For instance:
Menstrual Cycle: Hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can affect insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control.
Pregnancy: Pregnant women may experience changes in blood sugar levels due to hormonal changes.
5. Medications
Certain medications can affect blood sugar levels. For example:
Insulin: Used by individuals with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2 diabetes, insulin helps lower blood sugar levels.
Oral Medications: Various oral medications can increase insulin sensitivity or decrease glucose production in the liver.
6. Illness and Infection
Illness and infections can cause blood sugar levels to rise. The body releases stress hormones to fight infection, leading to increased glucose production. It is essential to monitor blood sugar closely during illness and adjust management strategies as needed.
Monitoring Average Daily Blood Sugar
1. Keeping a Blood Sugar Log
Maintaining a blood sugar log can help track daily levels and identify patterns. Key components of a blood sugar log include:
Date and Time: Record the date and time of each reading.
Blood Sugar Level: Write down the reading and whether it was fasting or postprandial.
Food Intake: Note what was eaten before testing.
Physical Activity: Include details of any exercise performed.
2. Understanding Patterns
Analyzing blood sugar logs can help identify trends and patterns, such as:
Time of Day Variations: Blood sugar levels may vary at different times of the day. Identifying these patterns can help with meal planning and medication timing.
Food Responses: Understanding how specific foods affect blood sugar levels can guide dietary choices.
3. Consulting with Healthcare Providers
Regular consultations with healthcare providers are essential for optimal diabetes management. They can help interpret blood sugar data, make necessary adjustments to treatment plans, and provide education on managing blood sugar levels effectively.
Maintaining Normal Average Daily Blood Sugar
1. Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is the foundation of blood sugar management. Key recommendations include:
Incorporating a Variety of Foods: Include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats in daily meals.
Monitoring Carbohydrate Intake: Use carbohydrate counting or portion control to manage carbohydrate intake.
Planning Meals and Snacks: Prepare meals in advance and avoid skipping meals to maintain steady blood sugar levels.
2. Regular Exercise
Engaging in regular physical activity can help maintain normal blood sugar levels. Recommendations include:
Aim for at Least 150 Minutes of Moderate-Intensity Exercise per Week: Activities like brisk walking, swimming, or cycling are beneficial.
Incorporate Strength Training: Resistance training two to three times per week can help improve insulin sensitivity.
3. Stress Management
Incorporating stress management techniques can help stabilize blood sugar levels. Effective strategies include:
Practicing Mindfulness or Meditation: These techniques can help reduce stress and promote relaxation.
Engaging in Regular Physical Activity: Exercise is a natural stress reliever.
4. Adequate Sleep
Getting enough sleep is essential for maintaining normal blood sugar levels. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night. Poor sleep can lead to insulin resistance and elevated blood sugar levels.
5. Regular Monitoring
Consistent monitoring of blood sugar levels is crucial for effective management. Regular checks allow for timely adjustments to diet, exercise, and medication. It is important to:
Use a Blood Glucose Meter or CGM: Choose a monitoring method that works best for your lifestyle and preferences.
Share Results with Healthcare Providers: Regularly discuss blood sugar readings with your healthcare team for personalized guidance.
See also: What is the Average Person’s Blood Sugar Level?
Conclusion
Understanding what constitutes a normal average daily blood sugar level is essential for effective diabetes management. Normal levels vary based on individual health, time of measurement, and dietary factors. Regular monitoring, a balanced diet, exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep are key components of maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
By implementing these strategies, individuals can take control of their blood sugar levels, reduce the risk of complications, and improve their overall health. Education and awareness play crucial roles in successful diabetes management, empowering individuals to make informed choices that promote a healthier lifestyle. Regular consultations with healthcare providers ensure personalized guidance and support on this journey toward optimal health.
Related topics:
How is Blood Sugar Measured in Blood Tests?