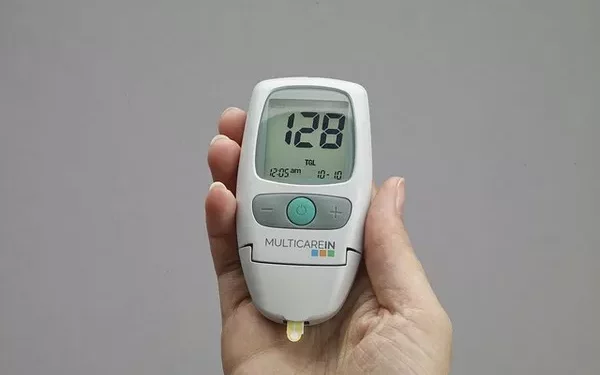
Hyperglycemia, commonly known as high blood sugar, occurs when there is an excess amount of glucose in the bloodstream. This condition is a hallmark of diabetes and can lead to both short- and long-term health complications if not properly managed. While diet plays a significant role in controlling blood sugar levels, what you drink is just as important. In this article, we’ll explore what individuals with hyperglycemia should drink to help manage their blood sugar levels, as well as beverages to avoid.
Understanding Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia occurs when the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use the insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar by enabling cells to absorb glucose. When insulin is insufficient or ineffective, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
The causes of hyperglycemia can vary, ranging from consuming too many carbohydrates to skipping insulin doses or experiencing illness or stress. Symptoms of hyperglycemia include frequent urination, increased thirst, fatigue, and blurred vision. If left untreated, chronic hyperglycemia can result in complications such as diabetic ketoacidosis, cardiovascular disease, and nerve damage.
Proper hydration is critical for individuals with hyperglycemia. Not only does it help manage blood sugar levels, but it also supports overall health. Here are the best drinks for managing hyperglycemia, along with some to avoid.
Water: The Best Choice
Why Water Is Important:
When it comes to managing hyperglycemia, water is the best drink you can consume. Water helps the body eliminate excess glucose through urine, and staying properly hydrated aids in overall health. Dehydration can lead to a rise in blood sugar levels because less water in the bloodstream makes the concentration of glucose higher. Drinking enough water is essential for helping kidneys flush out excess sugar and for supporting the body’s normal functions.
How Much Water Should You Drink?
The amount of water needed varies from person to person depending on factors such as age, activity level, and climate. However, a general guideline is to drink at least 8 glasses of water per day, and more if you are physically active or in hot conditions. For people with hyperglycemia, staying hydrated is even more critical.
Adding Flavor to Water:
If plain water feels too bland, you can infuse it with natural flavors. Adding slices of lemon, lime, cucumber, or a few mint leaves can make water more enjoyable to drink without adding any calories or sugar. Herbal teas (caffeine-free) that are brewed and chilled can also be a good option to keep your water intake interesting and flavorful.
Herbal Teas: A Calming, Sugar-Free Option
The Benefits of Herbal Teas:
Herbal teas are an excellent choice for people with hyperglycemia as they are typically caffeine-free, hydrating, and packed with beneficial antioxidants. Common herbal teas such as chamomile, peppermint, and hibiscus are not only soothing but also have potential health benefits.
For instance, some studies suggest that chamomile tea can help lower blood sugar levels. Hibiscus tea, on the other hand, has been shown to support cardiovascular health, which is essential for people with diabetes or those at risk of hyperglycemia-related complications.
Avoid Sweeteners:
When consuming herbal teas, it’s essential to avoid adding sweeteners such as sugar or honey, as these can spike blood glucose levels. If you need a bit of sweetness, consider using a small amount of a sugar substitute like stevia or monk fruit, both of which have minimal impact on blood sugar levels.
Green Tea: A Potentially Beneficial Beverage
Green Tea’s Impact on Blood Sugar:
Green tea is another healthy option for individuals with hyperglycemia. It contains compounds known as catechins, which are antioxidants that have been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and reduce blood sugar levels. Additionally, green tea has anti-inflammatory properties that may help reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications.
Caffeine Consideration:
It’s worth noting that green tea does contain caffeine, albeit less than coffee or black tea. While moderate amounts of caffeine are generally safe for most people with hyperglycemia, excessive caffeine intake can lead to dehydration and spikes in blood sugar levels. Therefore, it’s best to enjoy green tea in moderation—one to two cups per day should suffice.
Vegetable Juices: Low-Sugar and Nutrient-Dense
Benefits of Vegetable Juices:
Vegetable juices can be a good option for those with hyperglycemia, provided that they are made from non-starchy vegetables. Vegetables like spinach, kale, cucumber, and celery are low in carbohydrates and rich in nutrients, making them ideal ingredients for juices.
Avoid Fruit Juices:
Be cautious about using fruits in your juices, as even naturally occurring sugars in fruits can lead to a rapid rise in blood glucose levels. If you do want to add a bit of sweetness to your vegetable juice, consider using small amounts of low-sugar fruits like berries, which have a lower glycemic impact.
Make It Fresh:
It’s essential to make vegetable juices at home or opt for fresh, cold-pressed juices without any added sugars. Store-bought vegetable juices often contain added sugars, sodium, and preservatives that can negate the health benefits.
Coffee: Proceed with Caution
The Pros and Cons of Coffee:
Coffee has been the subject of various studies regarding its impact on blood sugar levels. Some studies suggest that regular coffee consumption may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Coffee contains antioxidants and polyphenols, which may enhance insulin sensitivity.
However, coffee can also have the opposite effect in some people by causing blood sugar levels to spike, particularly when consumed with added sugars or high-fat creamers. The caffeine in coffee can increase cortisol levels, which can, in turn, raise blood sugar levels in individuals who are more sensitive to its effects.
How to Enjoy Coffee Safely:
If you enjoy coffee, it’s crucial to drink it in moderation and to avoid adding sugar, flavored syrups, or high-fat creamers. Opt for black coffee or add a splash of unsweetened almond milk, and monitor your blood sugar levels to see how coffee affects you personally.
Milk Alternatives: A Low-Sugar Option
Unsweetened Almond, Soy, or Coconut Milk:
For those with hyperglycemia, choosing the right milk or milk alternative is important. Unsweetened almond milk, soy milk, and coconut milk are low in carbohydrates and free of added sugars, making them suitable choices for managing blood sugar levels. These alternatives are also low in calories, which is helpful for maintaining a healthy weight—another critical factor in managing hyperglycemia.
Avoid Flavored Varieties:
Be sure to avoid flavored or sweetened versions of these milk alternatives, as they often contain added sugars that can increase blood glucose levels.
Diluted Apple Cider Vinegar: A Traditional Remedy
Benefits of Apple Cider Vinegar:
Some studies suggest that apple cider vinegar may help improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood sugar levels after meals. Apple cider vinegar contains acetic acid, which is thought to slow the digestion of carbohydrates and prevent large spikes in blood sugar.
How to Use Apple Cider Vinegar:
To incorporate apple cider vinegar into your diet, dilute one to two tablespoons in a large glass of water. Drinking it before or after meals may help manage postprandial (after eating) blood sugar levels. However, it’s essential not to overdo it, as excessive consumption of vinegar can lead to stomach irritation and affect potassium levels in the body.
Electrolyte Drinks: Proceed with Caution
When to Use Electrolyte Drinks:
Electrolyte drinks, such as those used during sports or illness, can be beneficial if you are dehydrated or have lost electrolytes due to high blood sugar levels. However, many commercial electrolyte drinks contain added sugars and should be avoided by individuals with hyperglycemia unless they are specifically formulated for people with diabetes.
Choose Sugar-Free Versions:
If you need to replenish electrolytes, opt for sugar-free electrolyte drinks or those with minimal carbohydrates. These versions provide the necessary electrolytes without the risk of spiking blood glucose levels.
Drinks to Avoid
While knowing what to drink for hyperglycemia is essential, it’s equally important to be aware of beverages that should be avoided. These drinks can contribute to high blood sugar levels and exacerbate hyperglycemia:
Sugary Soft Drinks: Regular sodas are packed with high amounts of added sugars, which can cause a rapid and dramatic increase in blood sugar levels. They are among the worst beverages for individuals with hyperglycemia and should be completely avoided.
Fruit Juices: Even 100% fruit juices contain natural sugars that can raise blood glucose levels. Although they may seem like a healthier choice than sodas, fruit juices can still cause blood sugar spikes and are best avoided or consumed in very small quantities.
Energy Drinks: Energy drinks often contain large amounts of both caffeine and sugar. This combination can not only spike blood sugar levels but also lead to dehydration and increased heart rate, making them unsafe for people with hyperglycemia.
Sweetened Coffee Beverages: Specialty coffee drinks such as lattes, frappuccinos, or flavored coffee drinks are typically loaded with sugar and high-calorie ingredients, making them a poor choice for individuals with hyperglycemia.
See also: What’s Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Hyperglycemia
Conclusion
Managing hyperglycemia effectively requires careful consideration of both diet and beverage choices. Water remains the best drink for individuals with high blood sugar levels, as it helps maintain hydration and supports the body’s natural processes for eliminating excess glucose. Herbal teas, green tea, and unsweetened milk alternatives are also excellent choices for hydration and managing blood sugar levels.
Conversely, sugary drinks like sodas, fruit juices, and energy drinks should be avoided, as they can quickly raise blood glucose levels. Monitoring your response to certain beverages, staying hydrated, and choosing low-sugar, nutrient-dense options will help you better manage hyperglycemia and maintain optimal health.
By making thoughtful decisions about what you drink, you can significantly improve your ability to manage your blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of complications associated with hyperglycemia.
Related topics:
How Do You Calm Down Hyperglycemia?