Hyperglycemia, characterized by high levels of glucose in the blood, is a common condition often associated with diabetes. The relationship between hyperglycemia and weight loss is multifaceted and can be influenced by various physiological, metabolic, and lifestyle factors. This article delves into the mechanisms through which hyperglycemia can lead to weight loss, examines the underlying processes, and provides a comprehensive understanding of the condition’s impact on body weight.
Understanding Hyperglycemia
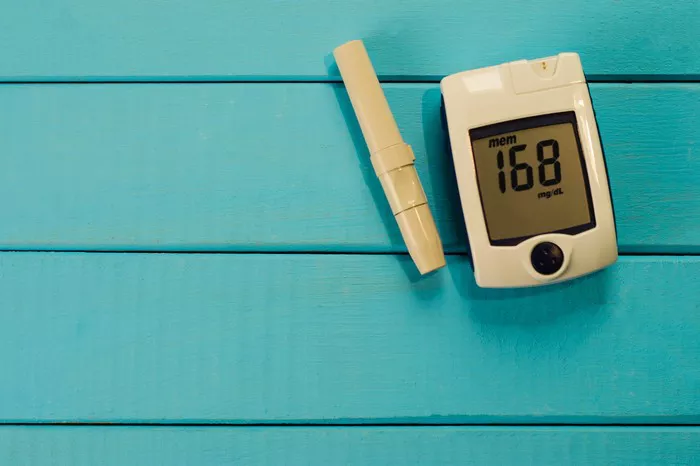
Hyperglycemia occurs when the body has an excess of glucose in the blood. This condition can arise due to insufficient insulin production by the pancreas (as seen in Type 1 diabetes), insulin resistance (as seen in Type 2 diabetes), or other health conditions that affect glucose metabolism. The primary symptoms of hyperglycemia include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and unexplained weight loss.
Insulin’s Role in Glucose Metabolism
Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, where it is used for energy. In the absence of sufficient insulin or when the body becomes resistant to insulin, glucose remains in the bloodstream, leading to hyperglycemia. This disruption in glucose metabolism has significant implications for body weight and overall health.
Mechanisms of Weight Loss in Hyperglycemia
Glucose Excretion in Urine
One of the primary mechanisms through which hyperglycemia can cause weight loss is through the excretion of glucose in the urine, a condition known as glucosuria. When blood glucose levels exceed the renal threshold (approximately 180 mg/dL), the kidneys cannot reabsorb all the filtered glucose, leading to its excretion in the urine. This process results in a loss of calories and subsequent weight loss.
Renal Threshold and Glucosuria
The renal threshold for glucose is the blood glucose concentration at which the kidneys start to excrete glucose into the urine. In individuals with hyperglycemia, this threshold is frequently exceeded, causing a significant loss of glucose and calories. Over time, this caloric deficit can contribute to noticeable weight loss.
Increased Metabolic Rate
Hyperglycemia can lead to an increased metabolic rate as the body attempts to manage elevated blood glucose levels. This heightened metabolic activity requires more energy, leading to the breakdown of fat and muscle tissue for fuel. Consequently, individuals with chronic hyperglycemia may experience weight loss as their bodies expend more energy to maintain homeostasis.
Metabolic Processes and Energy Expenditure
The body’s metabolic rate is influenced by various factors, including hormonal imbalances, stress, and the body’s efforts to regulate glucose levels. In the presence of hyperglycemia, the increased demand for energy can lead to the mobilization of fat stores and muscle protein, resulting in weight loss.
Lipolysis and Ketogenesis
In response to insufficient insulin or insulin resistance, the body may begin to break down fat stores through a process called lipolysis. This breakdown of fat releases fatty acids, which are then converted into ketones in the liver, a process known as ketogenesis. While ketones can be used as an alternative energy source, their production and accumulation can lead to weight loss and, in severe cases, diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
DKA is a serious complication of diabetes characterized by extremely high blood glucose levels, ketone production, and metabolic acidosis. It is more common in individuals with Type 1 diabetes but can also occur in Type 2 diabetes under certain conditions. DKA results in significant weight loss due to the combined effects of dehydration, glucosuria, and the catabolic state induced by ketogenesis.
Muscle Protein Breakdown
When the body is unable to utilize glucose effectively due to insulin deficiency or resistance, it may resort to breaking down muscle protein for energy. This catabolic process, known as proteolysis, contributes to muscle wasting and weight loss. The loss of muscle mass can further exacerbate metabolic imbalances and complicate the management of diabetes.
Proteolysis and Muscle Wasting
Proteolysis involves the breakdown of muscle proteins into amino acids, which can be used for gluconeogenesis (the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources) or as an energy source. This process is particularly pronounced in individuals with poorly controlled diabetes, leading to significant muscle wasting and weight loss.
Clinical Implications and Management
Monitoring and Managing Hyperglycemia
Effective management of hyperglycemia is crucial to prevent unintended weight loss and other complications. This involves regular monitoring of blood glucose levels, adherence to prescribed medications or insulin therapy, and lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.
Blood Glucose Monitoring
Frequent monitoring of blood glucose levels allows individuals with diabetes to manage their condition more effectively. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) and regular blood glucose testing can provide valuable insights into glucose patterns and help guide treatment decisions.
Nutritional Interventions
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in managing hyperglycemia and preventing weight loss. A balanced diet that includes adequate carbohydrates, proteins, and fats can help maintain stable blood glucose levels and support overall health.
Carbohydrate Management
Carbohydrates have a direct impact on blood glucose levels. Monitoring carbohydrate intake and choosing complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index can help prevent rapid spikes in blood glucose levels. Consistent carbohydrate intake throughout the day can also aid in maintaining stable glucose levels.
Protein and Fat Intake
Adequate protein intake is essential to prevent muscle wasting and support overall health. Including lean protein sources in the diet can help maintain muscle mass and promote satiety. Healthy fats, such as those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, can also provide a stable source of energy and support metabolic health.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is beneficial for managing hyperglycemia and preventing weight loss. Exercise enhances insulin sensitivity, promotes glucose uptake by muscles, and can help maintain muscle mass.
Types of Exercise
Both aerobic and resistance exercises are effective in managing hyperglycemia. Aerobic activities, such as walking, swimming, and cycling, can improve cardiovascular health and enhance insulin sensitivity. Resistance training, such as weightlifting or bodyweight exercises, can help maintain and build muscle mass.
Medication and Insulin Therapy
For individuals with diabetes, medication and insulin therapy are critical components of managing hyperglycemia. Adherence to prescribed treatments can help maintain blood glucose levels within the target range and prevent complications.
Insulin Therapy
Insulin therapy is essential for individuals with Type 1 diabetes and may be required for those with Type 2 diabetes who do not respond adequately to oral medications. Proper insulin dosing and administration can help regulate blood glucose levels and prevent hyperglycemia-related weight loss.
Oral Medications
Various oral medications are available to help manage blood glucose levels in individuals with Type 2 diabetes. These medications work through different mechanisms, such as increasing insulin sensitivity, stimulating insulin production, or inhibiting glucose production by the liver.
Addressing Complications
Addressing the underlying causes of hyperglycemia and its associated weight loss is crucial for preventing complications and improving overall health. This may involve a combination of lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, and regular monitoring by healthcare professionals.
Healthcare Professional Support
Regular consultations with healthcare professionals, including endocrinologists, dietitians, and diabetes educators, can provide valuable support and guidance in managing hyperglycemia. These professionals can help develop personalized treatment plans, monitor progress, and make necessary adjustments to therapy.
See also: What are the Causes of Sudden Hyperglycemia
Conclusion
Hyperglycemia can lead to weight loss through various mechanisms, including glucose excretion in urine, increased metabolic rate, lipolysis, ketogenesis, and muscle protein breakdown. Understanding these processes is essential for managing hyperglycemia and preventing unintended weight loss. Effective management involves regular blood glucose monitoring, nutritional interventions, physical activity, medication adherence, and support from healthcare professionals. By addressing the underlying causes of hyperglycemia and implementing appropriate management strategies, individuals with diabetes can achieve better control of their condition and maintain a healthy weight.
Related topics: