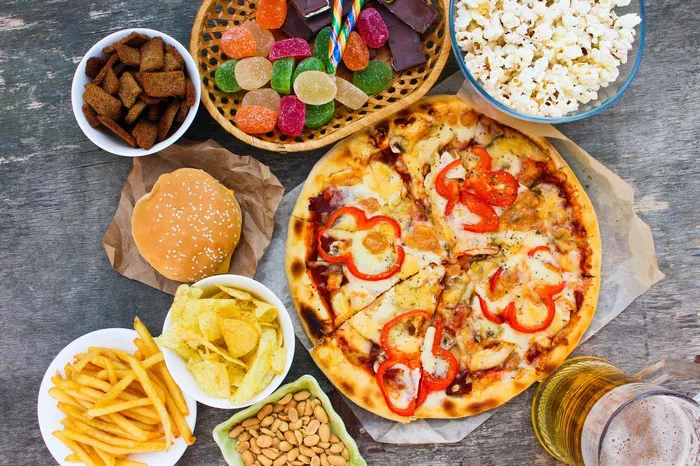
Type 2 diabetes is a prevalent chronic condition characterized by insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. While genetics and other factors play a role, lifestyle choices, including diet, are significant contributors to its development. Making informed dietary decisions can be pivotal in preventing or managing type 2 diabetes. In this article, we will explore the foods to avoid to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes and promote overall health.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes
Before delving into dietary recommendations, it’s essential to grasp the underlying mechanisms of type 2 diabetes. This condition occurs when the body either becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar effectively. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas, and its primary function is to facilitate the uptake of glucose into cells for energy production. When insulin resistance develops, glucose accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to high blood sugar levels, a hallmark of diabetes.
Dietary Factors in Type 2 Diabetes
Diet plays a crucial role in the development and management of type 2 diabetes. Certain foods can spike blood sugar levels rapidly, placing undue stress on the body’s insulin-producing mechanisms. Over time, consistent consumption of these foods can contribute to insulin resistance and increase the risk of developing diabetes. By understanding which foods to limit or avoid, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their health and mitigate the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Foods to Avoid
- Sugar-Sweetened Beverages: One of the primary culprits behind rising obesity and type 2 diabetes rates is the consumption of sugary drinks. These beverages, including soda, fruit juices, and energy drinks, are loaded with added sugars and offer little to no nutritional value. The rapid influx of sugar into the bloodstream can overwhelm the body’s insulin response, leading to insulin resistance over time. Opting for water, herbal teas, or unsweetened alternatives is a healthier choice to support blood sugar regulation.
- Processed and Refined Carbohydrates: Foods made from refined grains, such as white bread, white rice, and pasta, lack fiber and essential nutrients compared to their whole grain counterparts. Additionally, processed carbohydrates often contain added sugars and have a high glycemic index, meaning they cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels. Limiting intake of these refined carbohydrates can help stabilize blood sugar levels and reduce the risk of insulin resistance.
- Sweets and Desserts: Indulging in sweets and desserts, such as cakes, cookies, pastries, and candies, can significantly contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes. These treats are typically high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and calories, making them a double threat to metabolic health. While occasional consumption in moderation may be permissible, regularly indulging in sugary desserts can sabotage efforts to prevent diabetes and maintain a healthy weight.
- Fried Foods: Fried foods, including french fries, fried chicken, and doughnuts, are often high in unhealthy fats, calories, and refined carbohydrates. The frying process not only adds excess calories but also produces harmful compounds called advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which have been linked to insulin resistance and inflammation. Choosing baked, grilled, or steamed options over fried foods can promote better metabolic health and reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.
- Processed Meats: Processed meats, such as bacon, sausage, hot dogs, and deli meats, are associated with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes and other chronic conditions. These meats undergo processing methods like smoking, curing, or salting, often resulting in the addition of preservatives and high levels of sodium. Furthermore, they may contain harmful additives like nitrates and nitrites, which have been linked to insulin resistance and inflammation. Opting for lean sources of protein, such as poultry, fish, tofu, or legumes, can be a healthier alternative.
- Highly Processed Foods: Many packaged and convenience foods, including chips, crackers, sugary cereals, and microwave meals, are heavily processed and contain additives, preservatives, and refined ingredients. These ultra-processed foods are typically low in nutrients and high in unhealthy fats, sugars, and sodium. Regular consumption of highly processed foods has been linked to weight gain, insulin resistance, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Choosing whole, minimally processed foods whenever possible can support better metabolic health and overall well-being.
- Sugar-Sweetened Yogurts and Dairy Desserts: While yogurt can be a nutritious food rich in probiotics and protein, certain varieties are laden with added sugars and artificial flavorings. Flavored yogurts, yogurt drinks, and dairy-based desserts like ice cream and pudding can contribute to spikes in blood sugar levels and promote insulin resistance. Opting for plain, unsweetened yogurt and adding fresh fruit or a drizzle of honey for sweetness can be a healthier alternative.
- Sugar-laden Condiments and Sauces: Many condiments and sauces, such as ketchup, barbecue sauce, and sweet chili sauce, contain hidden sugars and high-fructose corn syrup. These added sugars can quickly add up, especially when used liberally, and contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. Choosing homemade or low-sugar alternatives or using herbs, spices, and vinegar for flavoring can help reduce sugar intake and support better blood sugar control.
Conclusion
In conclusion, making informed dietary choices is crucial for preventing type 2 diabetes and promoting overall health. By avoiding or limiting consumption of sugary beverages, processed and refined carbohydrates, sweets and desserts, fried foods, processed meats, highly processed foods, sugar-sweetened yogurts and dairy desserts, and sugar-laden condiments and sauces, individuals can reduce their risk of developing insulin resistance and diabetes. Instead, prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can support optimal metabolic health and contribute to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes. Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress, and getting adequate sleep are essential components of a comprehensive diabetes prevention strategy. By taking proactive steps to adopt a balanced and nutritious diet and lifestyle, individuals can empower themselves to prevent or manage type 2 diabetes and live a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Related topics:
I’m Diabetic: What Should I Eat?