Living with diabetes requires careful attention to diet and lifestyle factors to effectively manage blood sugar levels and prevent complications. In this article, we’ll explore how certain foods can impact diabetes management and provide practical tips for making healthier choices.
Diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management, as certain foods can cause blood sugar levels to spike, while others can help stabilize them. By making informed food choices, individuals with diabetes can better control their condition and improve overall health.
High-Sugar Foods
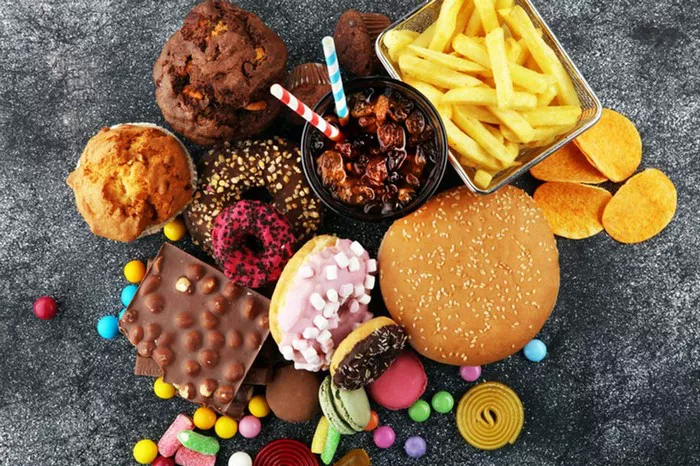
Foods high in sugar, such as sweetened drinks, candies, pastries, and desserts, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. These foods are quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, leading to a sharp increase in glucose levels followed by a crash. Limiting intake of high-sugar foods is essential for managing diabetes and preventing hyperglycemia.
Refined Carbohydrates
Refined carbohydrates, including white bread, white rice, and sugary cereals, are quickly broken down into sugar in the body, causing blood sugar levels to rise rapidly. These foods lack fiber and essential nutrients found in whole grains, making them poor choices for individuals with diabetes. Instead, opt for whole grains such as whole wheat bread, brown rice, quinoa, and oats, which provide sustained energy and help stabilize blood sugar levels.
Saturated and Trans Fats
Foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as fatty cuts of meat, fried foods, processed snacks, and baked goods, can worsen diabetes control and increase the risk of heart disease. These fats raise levels of LDL cholesterol (bad cholesterol) in the blood, leading to plaque buildup in the arteries and increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications. Choose healthier fats such as those found in nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil, which have heart-healthy benefits and can help improve insulin sensitivity.
High-Sodium Foods
High-sodium foods, including processed meats, canned soups, salty snacks, and fast food, can raise blood pressure levels, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke, especially for individuals with diabetes who are already at higher risk. To reduce sodium intake, opt for fresh or minimally processed foods, use herbs and spices to add flavor instead of salt, and read food labels carefully to identify hidden sources of sodium.
Portion Sizes and Frequency
Portion control is key for managing diabetes, even with healthier food choices. Pay attention to serving sizes and avoid oversized portions, which can lead to overeating and spikes in blood sugar levels. Additionally, spacing out meals and snacks evenly throughout the day can help prevent fluctuations in blood glucose levels and promote better glycemic control.
Healthy Alternatives
Making healthier food choices doesn’t mean sacrificing taste or satisfaction. Here are some practical substitutions for common ‘worst’ foods:
Instead of sweetened drinks, opt for water, herbal tea, or sparkling water with a splash of citrus.
Swap white bread and rice for whole grain varieties like whole wheat bread, brown rice, or quinoa.
Choose lean protein sources such as skinless poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and lentils instead of fatty cuts of meat or fried foods.
Snack on fresh fruits, vegetables with hummus, or unsalted nuts and seeds instead of salty snacks or processed chips.
Diabetes experts and nutritionists emphasize the importance of making gradual changes to your diet and focusing on overall dietary patterns rather than individual foods. Aim for a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support blood sugar control and overall well-being.
Personalized Nutrition Advice
Every individual with diabetes is unique, and dietary needs may vary based on factors such as age, weight, activity level, medication regimen, and blood sugar control goals. For personalized nutrition advice, consult with a registered dietitian or healthcare provider who can offer tailored recommendations to help you manage your diabetes effectively and achieve your health goals.
Conclusion
Making smart food choices is essential for managing diabetes and improving overall health. By avoiding high-sugar, refined carbohydrate, high-fat, and high-sodium foods and opting for healthier alternatives, individuals with diabetes can better control their condition and reduce the risk of complications. Remember to seek personalized nutrition advice from healthcare professionals to develop a dietary plan that meets your individual needs and supports your journey to better health.
Related Topics: