High blood sugar, or hyperglycemia, is a common concern for individuals with diabetes. When blood sugar levels rise above target ranges, it can lead to various symptoms and potential complications if left untreated. Managing high blood sugar requires prompt action to bring levels back within normal limits and prevent adverse outcomes. In this comprehensive article, we discuss immediate actions and strategies to take when blood sugar is too high, empowering individuals with diabetes to effectively manage hyperglycemia and safeguard their health.
Understanding Hyperglycemia:
Hyperglycemia occurs when blood sugar levels exceed recommended targets. In individuals with diabetes, this can happen due to factors such as insufficient insulin production, inadequate insulin action, excessive carbohydrate intake, stress, illness, or medication issues. Symptoms of hyperglycemia may include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, blurred vision, and difficulty concentrating. If left unaddressed, prolonged hyperglycemia can lead to diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS), both of which are serious medical emergencies.
Immediate Actions When Blood Sugar is Too High:
When faced with high blood sugar levels, prompt action is essential to prevent complications and bring glucose levels back within target ranges. Here are immediate steps to take:
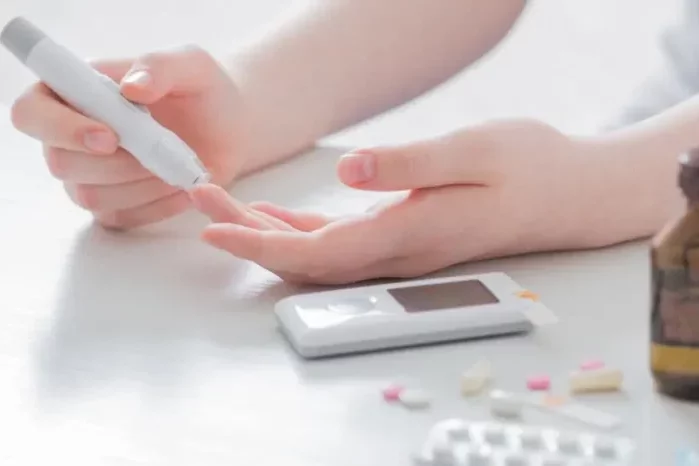
1. Check Blood Sugar: Use a glucose meter to measure blood sugar levels and confirm hyperglycemia. This helps determine the severity of the situation and guides subsequent actions.
2. Hydrate: Drink water or other non-caloric, caffeine-free fluids to help flush out excess glucose through increased urination. Staying hydrated can also alleviate symptoms of dehydration associated with high blood sugar.
3. Insulin Administration: If you use insulin, follow your healthcare provider’s instructions for administering additional doses or corrections to bring blood sugar levels down. Rapid-acting insulin may be prescribed for this purpose.
4. Physical Activity: Engage in light to moderate physical activity, such as walking, to help lower blood sugar levels. Exercise helps the body utilize glucose for energy and can improve insulin sensitivity.
5. Avoid High-Carbohydrate Foods: Refrain from consuming high-carbohydrate foods or sugary beverages, as they can further elevate blood sugar levels. Opt for low-carbohydrate, high-fiber options to help stabilize glucose levels.
6. Monitor Ketones: If you have type 1 diabetes or are at risk of DKA, monitor ketone levels using urine or blood ketone testing strips. Elevated ketone levels indicate insufficient insulin and may require medical intervention.
7. Seek Medical Assistance: If blood sugar levels remain persistently high despite intervention efforts, or if you experience symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis (such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or fruity breath odor), seek immediate medical attention.
Strategies for Managing Hyperglycemia:
In addition to immediate actions, adopting long-term strategies can help prevent episodes of high blood sugar and promote overall glycemic control:
1. Medication Adherence: Take prescribed medications, including insulin and oral antidiabetic agents, as directed by your healthcare provider. Consistent medication adherence is crucial for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
2. Healthy Eating: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains while limiting processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-carbohydrate meals. Portion control and carbohydrate counting can help manage blood sugar levels.
3. Regular Physical Activity: Incorporate regular exercise into your routine, aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week, as recommended by guidelines. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
4. Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques such as mindfulness, deep breathing, yoga, or meditation to alleviate psychological stress, which can impact blood sugar levels.
5. Monitor Blood Sugar: Check blood sugar levels regularly, as recommended by your healthcare provider, and keep track of trends over time. This allows for timely adjustments to treatment regimens and helps identify patterns of hyperglycemia.
6. Stay Hydrated: Drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration and support kidney function. Avoid sugary beverages and excessive alcohol consumption, which can contribute to fluctuations in blood sugar levels.
7. Regular Healthcare Visits: Attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to review blood sugar readings, assess overall health status, and make any necessary adjustments to your diabetes management plan.
Conclusion:
Managing high blood sugar levels requires a proactive approach and prompt intervention to prevent complications and promote optimal health. By taking immediate actions such as checking blood sugar, staying hydrated, administering insulin as needed, and engaging in physical activity, individuals with diabetes can effectively manage hyperglycemia and mitigate associated risks. Adopting long-term strategies for healthy eating, regular exercise, stress management, and medication adherence further supports glycemic control and enhances overall well-being. With diligence, awareness, and collaboration with healthcare providers, individuals with diabetes can navigate hyperglycemic episodes and strive for optimal blood sugar management.